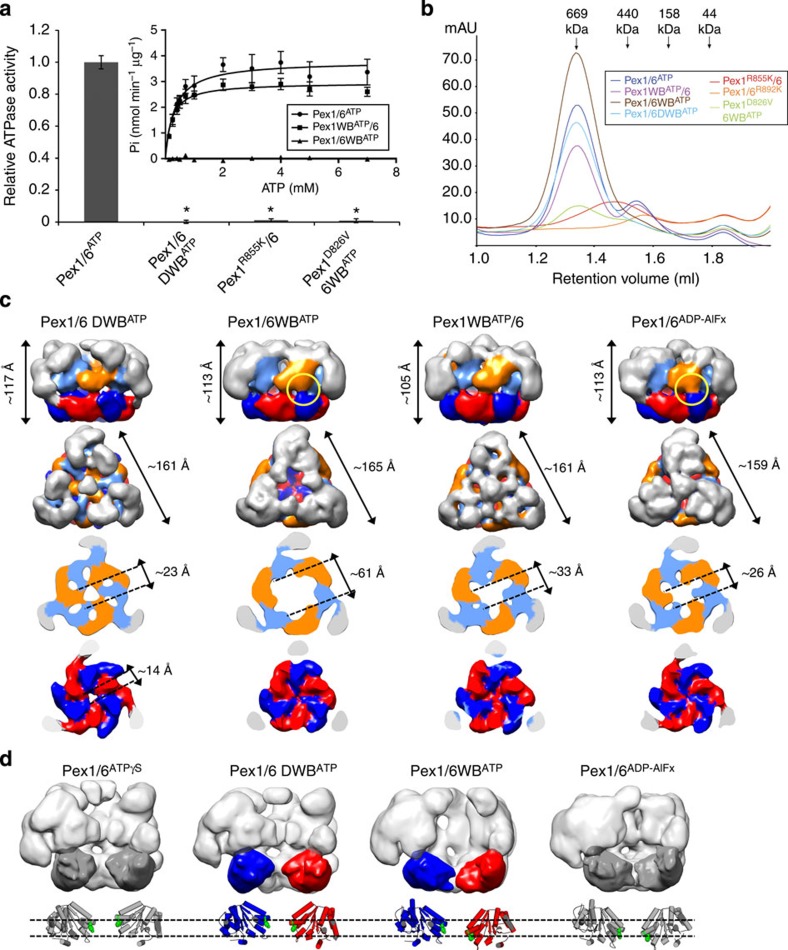
Figure 4. ATPase activity of Pex6 D2 domains drive conformational changes.
(a) ATPase activities of wild-type Pex1/6 (Pex1/6ATP), single Walker B (Pex1WBATP/6, Pex1/6WBATP) or double-Walker B mutants (Pex1/6 DWBATP) or Pex1 arginine finger (Pex1R855K/6) or ISS motif (Pex1D826V/6WBATP) mutants. Assays were performed in the presence of 1 mM ATP and 5 mM Mg2+ at 37 °C. Error bars represent s.d. of two independent experiments with five technical replicates each. *P<0.0001 in comparison with wild-type Pex1/6ATP (one-way ANOVA). Michaelis–Menten plot of enzyme activity of Pex1/6ATP, Pex1WBATP/6 or Pex1/6WBATP at various ATP concentrations (inset). Error bars represent s.d. of two independent experiments including three technical replicates. (b) Size-exclusion chromatography A290 nm profiles of purified Pex1/6 complexes used for ATPase activity assays. (c) EM reconstructions of double- (Pex1/6 DWBATP) or single- (Pex1/6WBATP, Pex1WBATP/6) Walker B complexes in the presence of ATP as side views (upper row), followed by top views and cross-sections of the D1 and D2 rings (lower rows). (d) Side-view surface representation as in Fig. 3a. Underneath, a cartoon representation based on rigid body fits of homology models into negative stain EM maps is shown. Pex1/6ATPγS and Pex1/6ADP-AlFx are depicted in grey for comparison. Domains are coloured according to Fig. 1d. Green spheres depict residues Pex1F771 and Pex6Y805.