Figure 2.
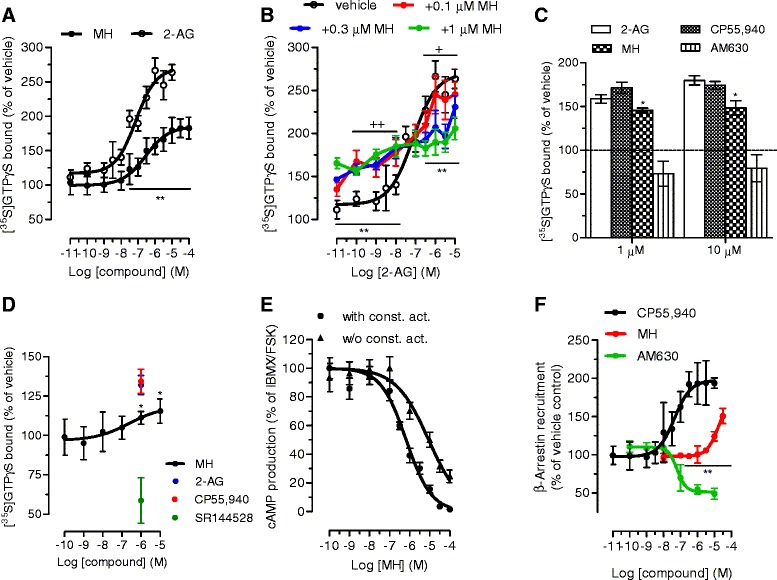
Modulation of CB2 receptor activity by MH. (A) [35S]GTPγS binding assay was performed in stably hCB2 receptor overexpressing CHO-K1 membranes, in the presence of different concentrations of MH and 2-AG alone or (B) in combination. The same experiments were performed in endogenously CB2 expressing (C) HL60 cells and (D) mouse spleen membranes. (E) Inhibition of forskolin-induced cAMP formation by MH in CHO-hCB2 cells transfected with pGloSensorTM 22-F plasmid. The experiments were performed in the presence (circles) and in the absence (triangles) of constitutive activity. (F) β-arrestin recruitment induced by increasing concentrations of MH, CP55,940, and AM630, measured in PathHunter® β-arrestin cells (CHO-K1-HOMSA-CNR2). ** P < 0.01 MH vs. 2-AG (Figure 2A); ** P < 0.01 MH (1 μM) plus 2-AG vs. 2-AG, ++ P < 0.01, + P < 0.05 MH (0.3 μM) plus 2-AG vs. 2-AG (Figure 2B). * P < 0.05 MH vs. 2-AG and CP55,940 (Figures 2C, D).** P < 0.01 MH vs. CP55,940 (Figure 2F).
