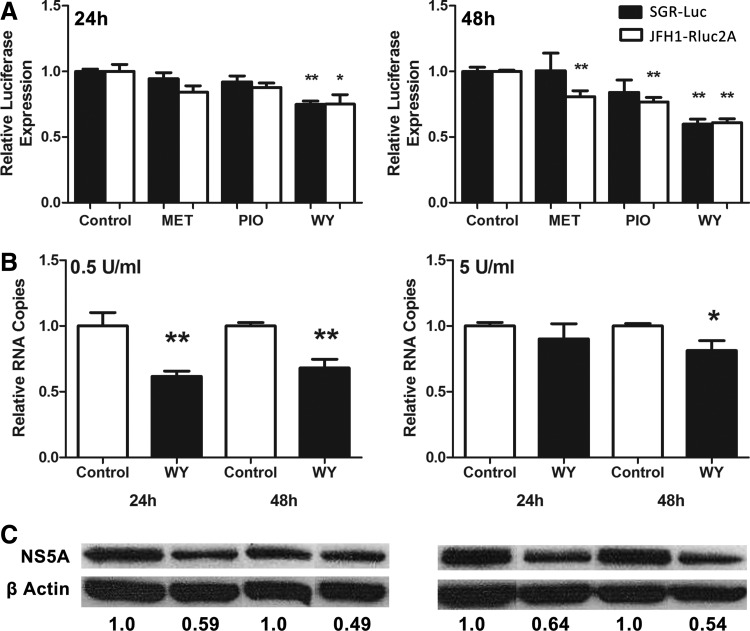
FIG. 1.
PPARα agonists and other insulin-sensitizing drugs enhance the antiviral effects of IFN-α against HCV. HCV infected Huh-7 cells were pretreated with different insulin-sensitizing drugs for 24 h, treated with IFN-α (10 U/mL), then HCV replication determined by luciferase reporter output (A). Luminescence in mock-treated cells was normalized to 1 at each time point and compared with treated cells. At 24 and 48 h post IFN-α treatment, WY-14643 alone significantly decreased viral replication compared with control in SGR-luc-containing cells (black) and JFH1-Rluc2A-infected cells (white). To confirm these results, JFH1-infected Huh-7 cells were pretreated with WY-14643 for 24 h, then treated with IFN-α. HCV RNA was measured by qPCR following treatment with 0.5 or 5 U/mL IFN-α (B). Significant reduction in JFH1 replication was observed at both 24 and 48 h using 0.5 U/mL IFN with WY-14643 pretreatment, and at 48 h using 5 U/mL IFN with WY-14643 pretreatment. A maximum ∼40% reduction in HCV protein expression (NS5A) was confirmed by western blot and densitometry analysis of NS5A protein expression (C). Graphs and western blot densitometry demonstrate an average of 3 experimental replicates (*P<0.05, **P<0.01). HCV, hepatitis C virus; IFN, interferon; qPCR, quantitative PCR; SGR, sub-genomic replicon.