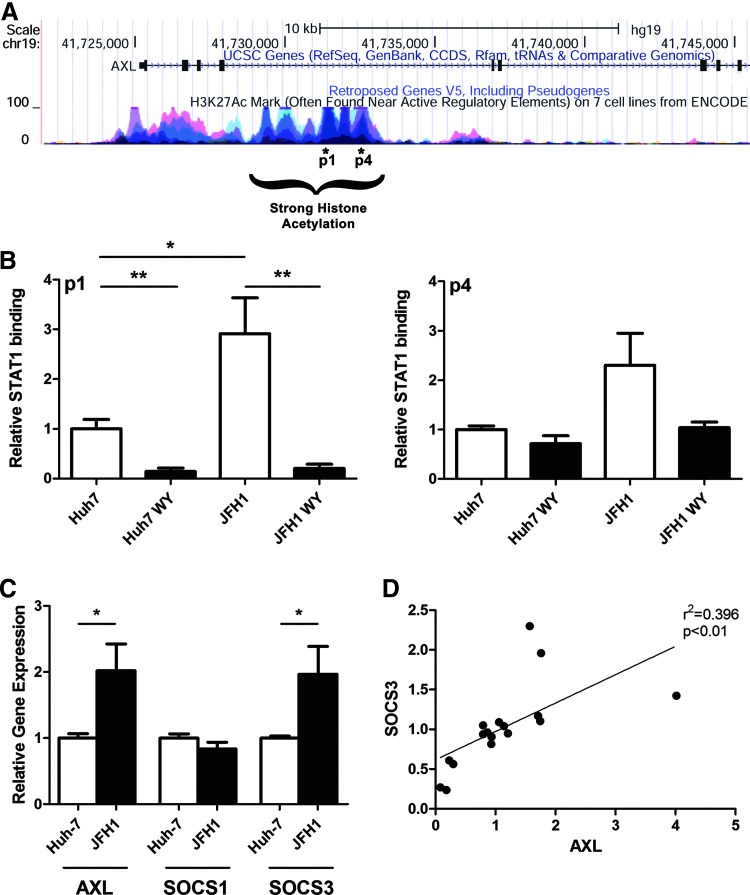
FIG. 7.
HCV-induced AXL expression is reduced by WY-14643. (A) The UCSC genome browser was used to identify 2 potential STAT1 binding sites (p1 and p4) in the fourth intron of AXL. (B) Binding of STAT1 to AXL was analyzed by ChIP followed by qPCR. JFH1-infected and mock-infected Huh-7 cells were treated with IFN-α (50 U/L), with or without pretreatment with the PPARα agonist WY-14643. In response to IFN-α treatment, STAT1 binding was reduced by ∼80% in cells pretreated with WY-14643 (P<0.01). STAT1 binding to AXL p1 (P<0.05) and p4 (N.S.) was increased by ∼2-fold in JFH1-infected cells compared with mock-infected Huh-7 cells (2 experimental ChIP replicates, performed in duplicate). (C) AXL expression in JFH1-infected cells was increased by a similar 2-fold over Huh-7 cells. SOCS3 expression was also significantly upregulated in JFH1-infected cells, and correlated with AXL expression (D), suggesting that AXL may induce SOCS3 expression in hepatocytes, as previously demonstrated in dendritic cells (Rothlin and others 2007). Graphs demonstrate an average of 3 experimental replicates (*P<0.05; **P<0.01). ChIP, chromatin immunoprecipitation; N.S., not significant.