Fig. 3.
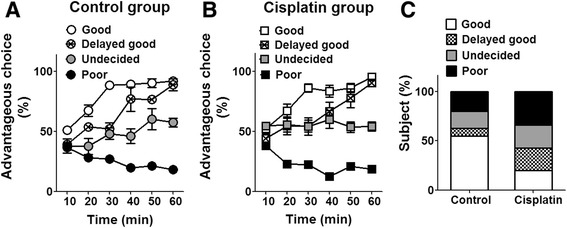
Changes in decision-making behavior induced by cisplatin using a rat Iowa gambling task. a – b Time course of percentage of advantageous choices for good (white), delayed good (grid), undecided (30 % gray) and poor (black) decision-makers during a 60 min RGT testing in control (A circles) and cisplatin (B squares) rats. Within the first 10 min, rats chose equally between advantageous and disadvantageous choices. They then quickly developed four distinct subgroups based on the percentage of advantageous choices during the 60 min test (>70 % preference of advantageous choices at 30 min and in the last 20 min for good decision-maker, < 70 % preference of advantageous choices at 30 min and > 70 % preference in the last 20 min for delayed good decision-maker, < 30 % in the last 20 min for poor decision-maker, and 30 - 70 % in the last 20 min for undecided maker). c Proportions of good performers (white bar), delayed good performers (grid bar), undecided behavior (30 % gray bar) and poor decision-making (black bar) for control group and cisplatin group. Advantageous choices (%) = numbers of nose-poke for choices (C + D) / numbers of nose-poke for choices (A + B + C + D) * 100 %. n = 24 for control group, n = 35 for cisplatin group
