Fig. 3.
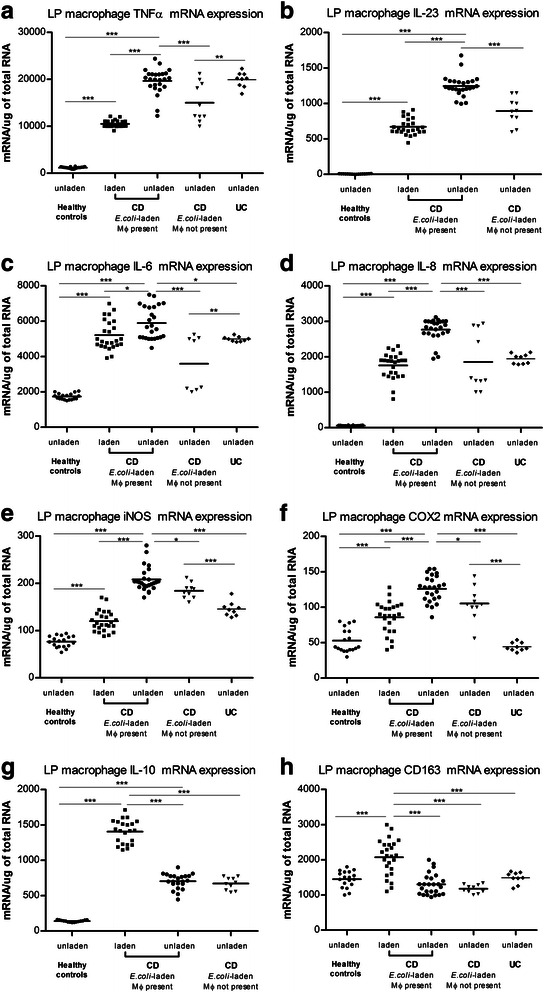
Cytokine and surface marker mRNA levels in healthy controls, CD patients with E. coli laden macrophages, CD patients without E. coli laden macrophages and UC patients. Fig. 3(a) From left to right: Healthy controls (n = 18); LP macrophages have low TNFα mRNA expression. Inflamed mucosal biopsies from CD patients with both E. coli-laden and unladen macrophages present (n = 25); E. coli-unladen macrophages had higher mean TNFα mRNA expression (P < .001) than E. coli-laden macrophages. CD patients without E. coli-laden macrophages (n = 10); TNFα mRNA expression of E. coli-unladen macrophages were lower than in E. coli-unladen macrophages from the 25 CD patients in whom both E. coli-laden and unladen were present (P < .001). UC patients (n = 9); E. coli-unladen LP macrophages showed elevated TNFα mRNA levels. Fig 3(b) to (f): Expression of other proinflammatory cytokines (IL-23, IL-6, IL-8) and iNOS is similar to the pattern of TNFα expression in samples from each subject group. Fig. 3 (g) Expression of COX2 is similar to the pattern of TNFα in each group but is lower in UC than in CD. In distinction to the pattern of TNFα expression, Fg. 3 (g) and 3(h) demonstrate that IL-10 and CD-163 mRNA expression are higher in E. coli-laden than E. coli-unladen macrophages in CD (for each; P < .001). *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001. Comparisons of means made with one-way ANOVA and Games-Howell post-hoc pair-wise comparisons. There was no UC data for IL-23 or IL-10. Only one UC patient had E. coli-laden macrophages (cytokine data not shown)
