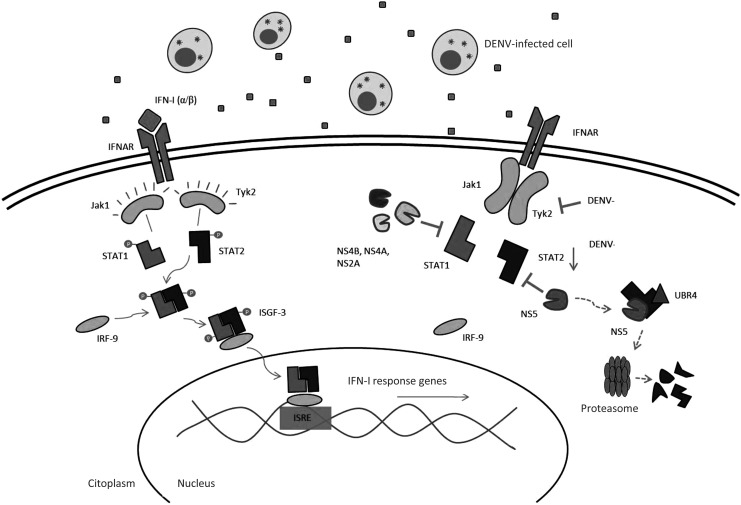
FIG. 2.
DENV inhibits IFN-I signaling. IFN-α/β binding to its receptors, known as IFANR, leads to the activation of the tyrosine kinases, Janus kinase 1 (Jak1) and Tyrosine kinase 2 (Tyk2), which once activated form a heterodimer that binds to the DNA-binding protein IRF-9 to finally form the transcription factor, IFN-stimulated gene factor 3 (ISGF-3). This transcription factor translocates to the nucleus where it stimulates the expression of hundreds of IFN-I-stimulated genes (ISGs). DENV inhibits Tyk2 activation and also STAT1 phosphorylation through its proteins, NS2A, NS4A, and NS4B. DENV also downregulates the expression of STAT2 and its NS5 protein blocks STAT2 phosphorylation. Finally, NS5 degrades STAT2 through a proteosoma-dependent mechanism, binding to the cellular protein ubiquitin protein ligase E3 component recognin 4 (UBR4).