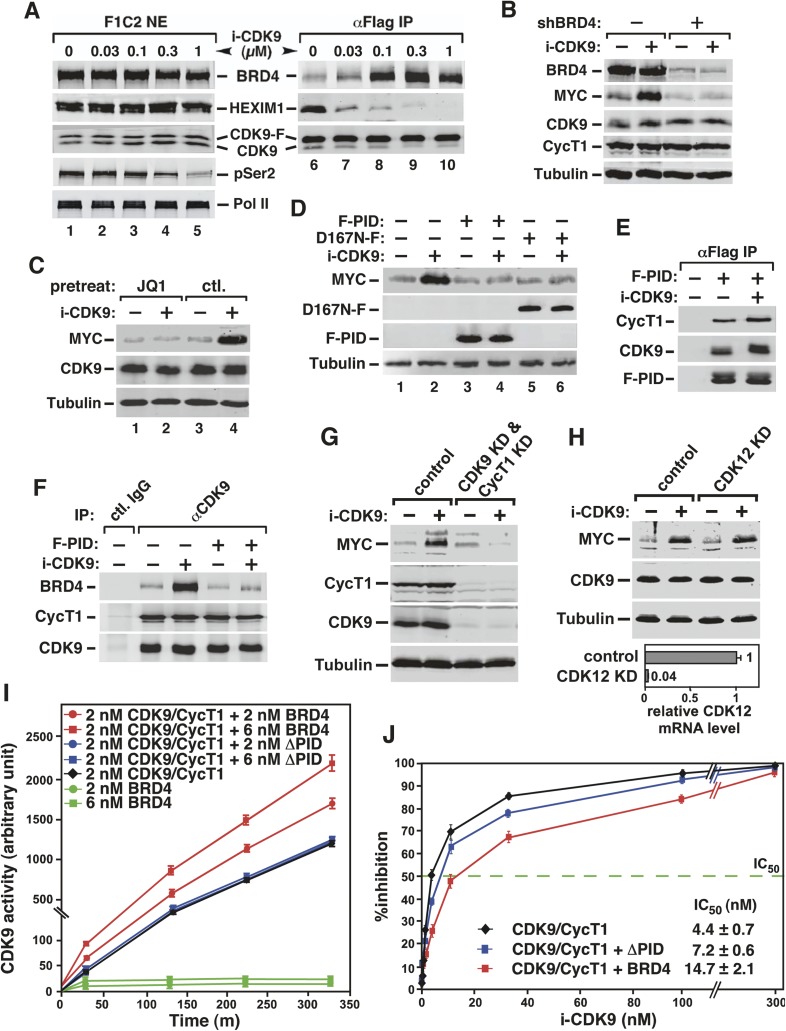
Figure 4. Activation of MYC transcription by i-CDK9 depends on induced transfer of kinase-active P-TEFb from 7SK snRNP to BRD4, binding of the BRD4-P-TEFb complex to acetylated MYC chromatin template, and BRD4-mediated increase in CDK9's catalytic activity and resistance to inhibition.
(A) The HeLa-based F1C2 cells stably expressing CDK9-F were incubated with the indicated concentrations of i-CDK9. Nuclear extracts (NE) and the anti-CDK9-F immunoprecipitates (IP) derived from NE were analyzed by immunoblotting to detect the indicated proteins. (B and C) Lysates of HeLa cells expressing the BRD4-specific shRNA (shBRD4; B) or pretreated with JQ1 or the control enantiomer (ctl.; C) were incubated with (+) or without (−) i-CDK9 and analyzed by immunoblotting for the indicated proteins. (D–H) Cells were first transfected with plasmids expressing F-PID (D, E and F), D167N-F (D), or shCycT1 (G) or transfected with siRNAs specific for CDK9 (G) or CDK12 (H) and then treated with i-CDK9 or DMSO (−). NE (D, G and H) and immunoprecipitates (IP) obtained from NE with anti-Flag mAb (E) or anti-CDK9 antibodies or rabbit total IgG (F) were examined by immunoblotting for the indicated proteins. The relative CDK12 mRNA levels were analyzed by qRT-PCR at the bottom in H, with the level in cells transfected with a control siRNA set to 1. (I and J) In vitro kinase reactions containing a synthetic Pol II CTD peptide (CDK7tide) as the substrate and CDK9-CycT1 (Invitrogen) as the kinase were conducted in the presence of the indicated amounts of WT or ∆PID BRD4. Phosphorylation of the peptide was measured over the indicated time periods and plotted in I, with the error bars representing mean ± SD from three independent experiments. The indicated amounts of i-CDK9 were added to the reactions in J, and its inhibition of CDK9 phosphorylation of the peptide was measured and plotted with the inhibitory IC50 shown.
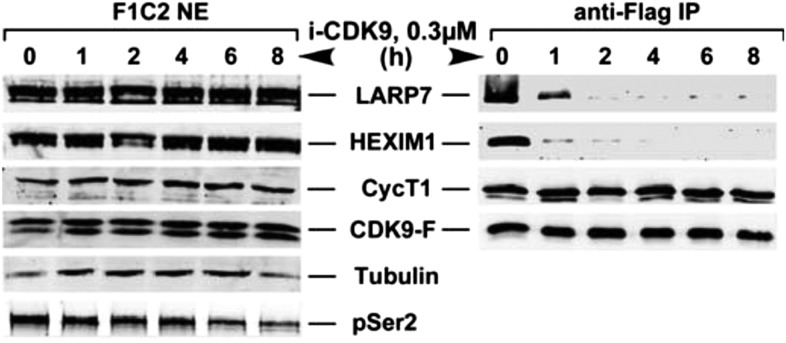
Figure 4—figure supplement 1. i-CDK9 (0.3 μM) induces disruption of 7SK snRNP at a time point much earlier than that required to cause about 50% reduction in global pSer2.
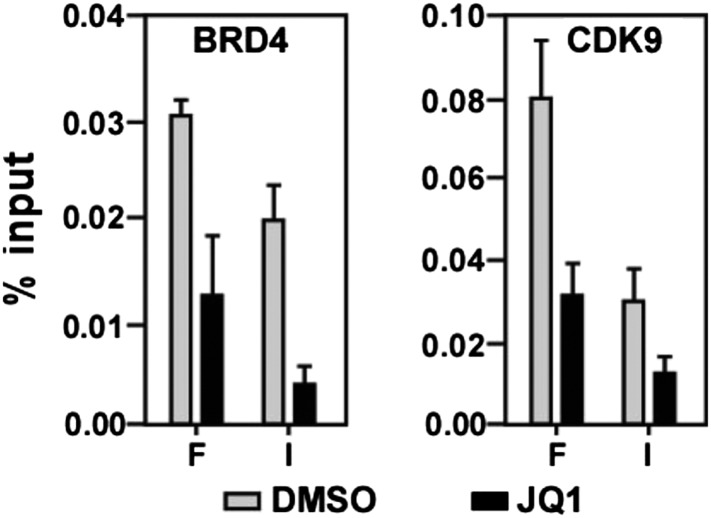
Figure 4—figure supplement 2. JQ1 decreases associations of both BRD4 and CDK9 with the MYC locus.
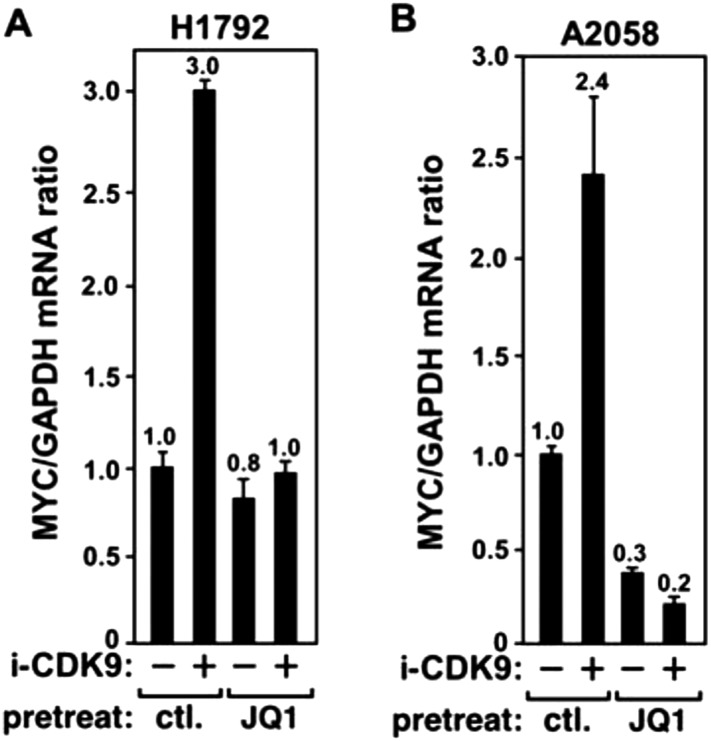
Figure 4—figure supplement 3. JQ1 blocks the i-CDK9-induced MYC expression in H1792 and A2058 cells.
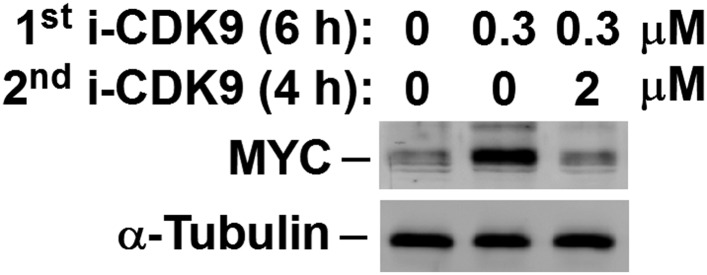
Figure 4—figure supplement 4. MYC induction by 0.3 μM i-CDK9 can be subsequently shut off by 2 μM of the drug.