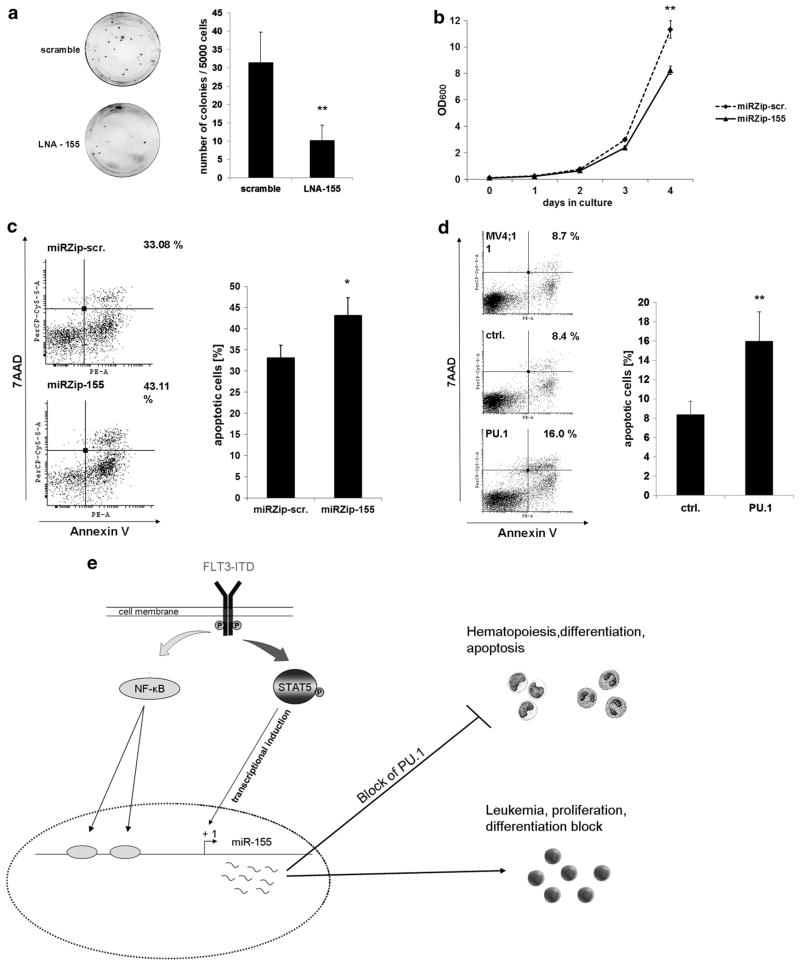
Figure 6.
MiR-155 expression is important for FLT3-ITD induced proliferation and survival in AML. (a) LNA-mediated block of miR-155 in 32D cells, stably expressing FLT3-ITD, reduces clonal growth. Colony-forming assays were performed in methylcellulose medium to analyze influence of miR-155 knockdown on the clonal growth capacity. The 32D FLT3-ITD cells were transfected with LNAs (200 nM) against miR-155 or scramble control. Four hours after transfection, cells were plated in triplicate at a density of 5000 cells per dish. Colonies were analyzed on day 12. Each bar represents the average ±s.d. of three independent experiments. (b) Knockdown of miR-155 reduces proliferation of FLT3-ITD associated 32D cells. Growth curve of 32DFLT3-ITD cells stably infected with miRZip-155 for miR-155 knockdown or miRZip-scr as control. A total of 105 cells were seeded and cultured for 4 days. Optical density was measured every day by 600 nm to detect proliferation. The data represents the average ±s.d. of three independent experiments (**P ≤ 0.01). (c) MiR-155 knockdown in FLT3-ITD-associated MV4;11 cells enhances apoptosis. Flow cytometric analyses for Annexin V expression in MV4;11 cells 48 h after transfection with miRZip-scr or miRZip-155. The bars represent the average ±s.d. of three independent experiments (*P ≤ 0.05). (d) PU.1 overexpression in FLT3-ITD-associated MV4;11 cells induces apoptosis. Flow cytometric analyses for Annexin V expression in MV4;11 cells 24 h after transfection of control or PU.1. The bars represents the average ±s.d. of three independent experiments (**P ≤ 0.01). (e) A model depicting transcriptional regulation and function of miR-155 in FLT3-ITD-associated AML. FLT3-ITD induces the oncogenic miR-155 by STAT5 and NF-κB. High expression of miR-155 decreases PU.1 protein level, which leads to differentiation block, proliferation and transformation.