Figure 3.
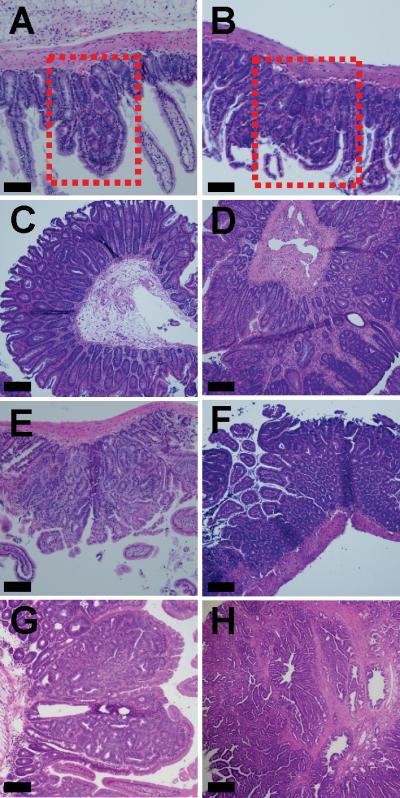
Histopathology of intestinal tumor development associated with Blm/BLM in ApcMin/+ mice. A-F, Although BLM-Tg reduces adenoma numbers on the ApcMin/+ background, it does not alter the underlying histopathology of emerging adenomas: A, ApcMin/+ jejunum, boxed area highlights GIN; B, ApcMin/+;BLMT/T jejunum, boxed area highlights GIN; C, ApcMin/+;BLMT/T cecum, adenoma; D, ApcMin/+;BLM+/T colon, adenoma; E, ApcMin/+;BLM+/T jejunum, adenoma; F, ApcMin/+;BLMT/T ileum, adenoma. G-H, Blm haplo-insufficiency drives tumor development and accelerates the development of intestinal adenomas with high-grade dysplasia and invasive carcinoma: G, ApcMin/+;BlmCin/+, adenoma with high-grade dysplasia; H, ApcMin/+;BlmCin/+, invasive adenocarcinoma. All sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Scale bars each represent 100 μm.
