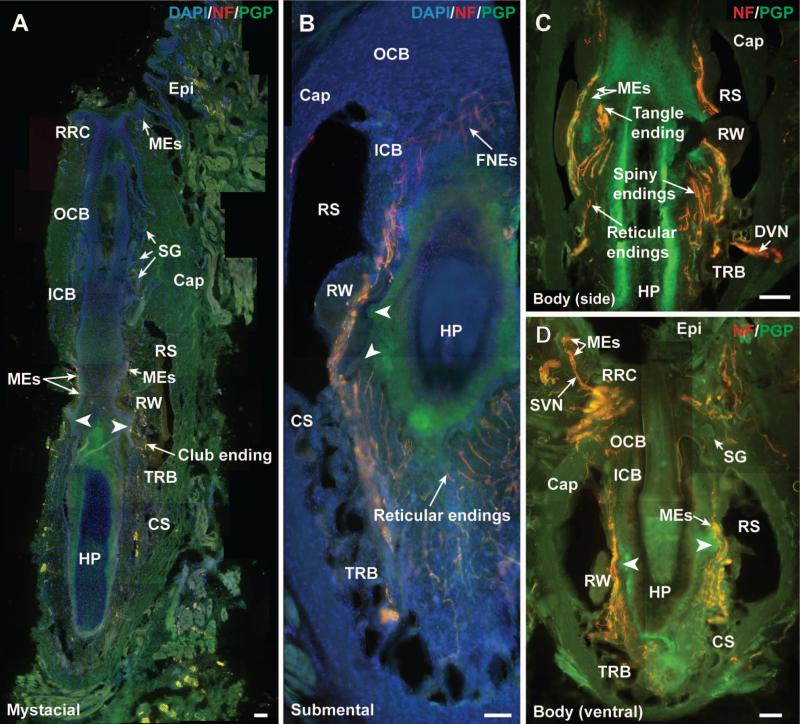
Figure 3.
Longitudinal sections just off of the central axis of rock hyrax FSCs illustrating the overall structure, prominent ring sinus and ringwulst, and types of nerve endings present in facial and post-facial body regions. A) mystacial, B) submental, C) lateral body, and D) ventral body region FSCs exhibit the characteristics of true vibrissae. Arrowheads indicate mesenchymal bulges at the ring sinus level. Immunolabeling shown consisted of DAPI (blue, nuclear marker; 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole), NF200 (red; 200kD subunit of neurofilament), and PGP (green, universal neuronal marker; protein gene product 9.5). Scale bars=300μm (A-D). Cap = capsule, CS = cavernous sinus, Epi = epidermis, FNEs = free nerve endings, HP = hair papilla, ICB = inner conical body, MEs = Merkel endings, OCB = outer conical body, RRC = rete ridge collar, RS = ring sinus, RW = ringwulst, SG = sebaceous gland, TRB = trabeculae.