Fig. 7. Effect of HY-antigen distribution on HY-specific iTreg-medicated protection.
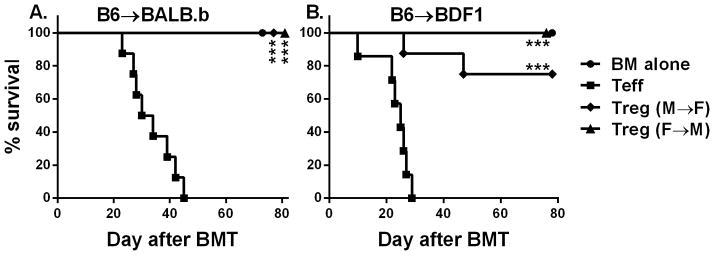
(A) Male → female or female → male BM chimeras were generated using BALB.b mice as described in “Material and Method”. These BM chimeras were lethally irradiated again and divided into 2 cohorts, each of which were transferred with TCD-BM alone or plus 25 x 106/mouse total splenocytes from normal B6 donors. HY-specific iTregs were also included at 4 x 106/mouse into donor graft at the day of BMT for some recipients. Recipient survival is shown, and the data represent 5–8 mice in each group. (B) Male → female or female → male BM chimeras were generated using BDF1 mice as described in “Material and Method”. These BM chimeras were lethally irradiated again and divided into 2 cohorts, each of which were transferred with TCD-BM alone or plus 4 x 106/mouse CD25-depleted total T cells from normal B6 donors. HY-specific iTregs were also included at 2 x 106/mouse into donor graft at the day of BMT for some recipients. Recipient survival is shown, and the data represent 7–8 mice in each group. Asterisk indicates statistical significance: *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001
