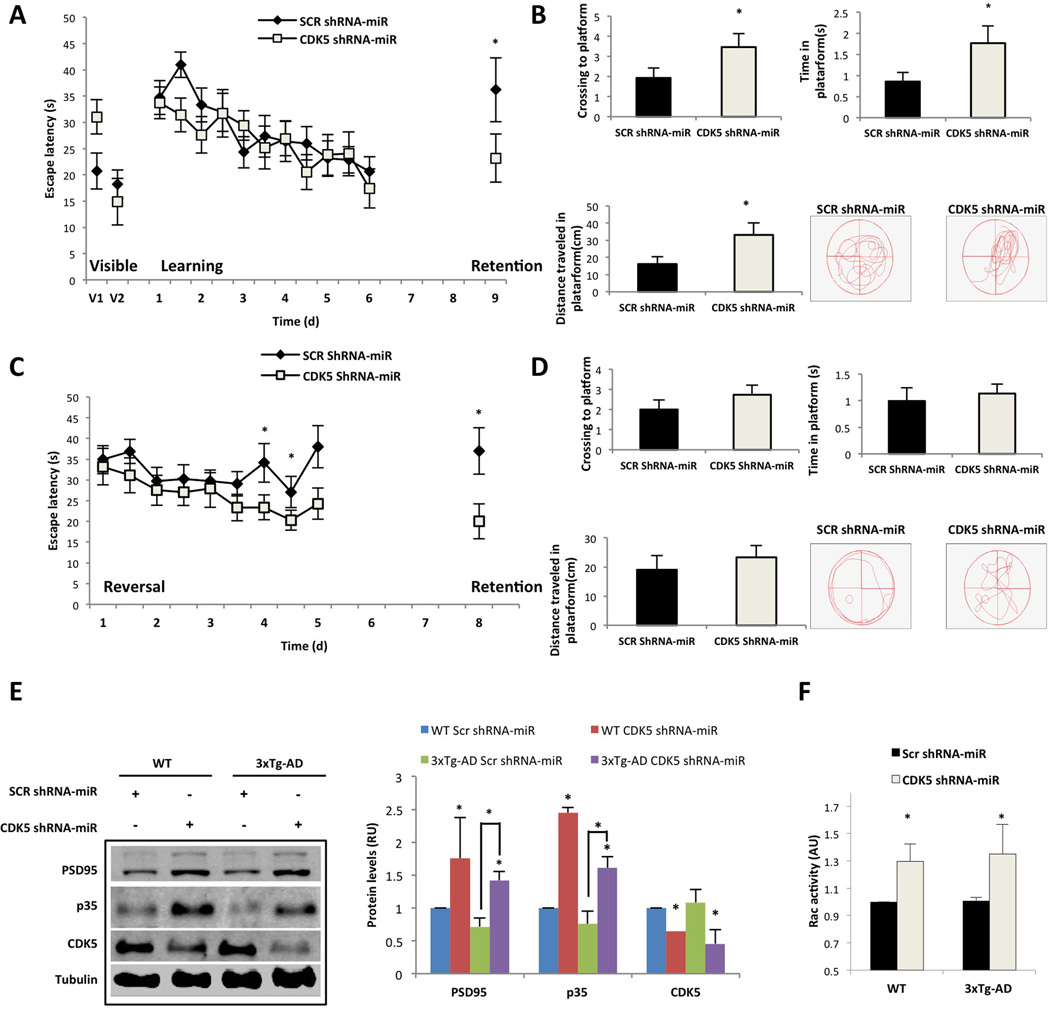
Figure 6.
CDK5 miR improves learning and memory in 3xtg-AD mice that exhibit increased p35 and active Rac. The test procedure comprised the (A) visible test, learning and retention with a hidden platform. (B) Spatial acuity was represented as the number of platform area crossings and the time and distance travelled to the hidden platform location in the retention test. (C and D) Reversal learning test with a second retention. Analysis of the latency in C and spatial acuity measurements in D. Data are presented as the mean ± S.E.M. n = 14. *, P < 0.05. (E) PSD95, p35 and CDK5 protein levels from the hippocampus assessed via Western blotting. βIII-tubulin was used as the loading control. Relative units = RU. F) Rac activity was quantified by ELISA (λ = 490 nm). The data are presented as the means ± SEM from n = 5 per duplicate. The values were normalised to the control. *, P < 0.05; Student’s t-test (A, B, C, D and F). *, P < 0.05; ANOVA with Tukey’s test for E.