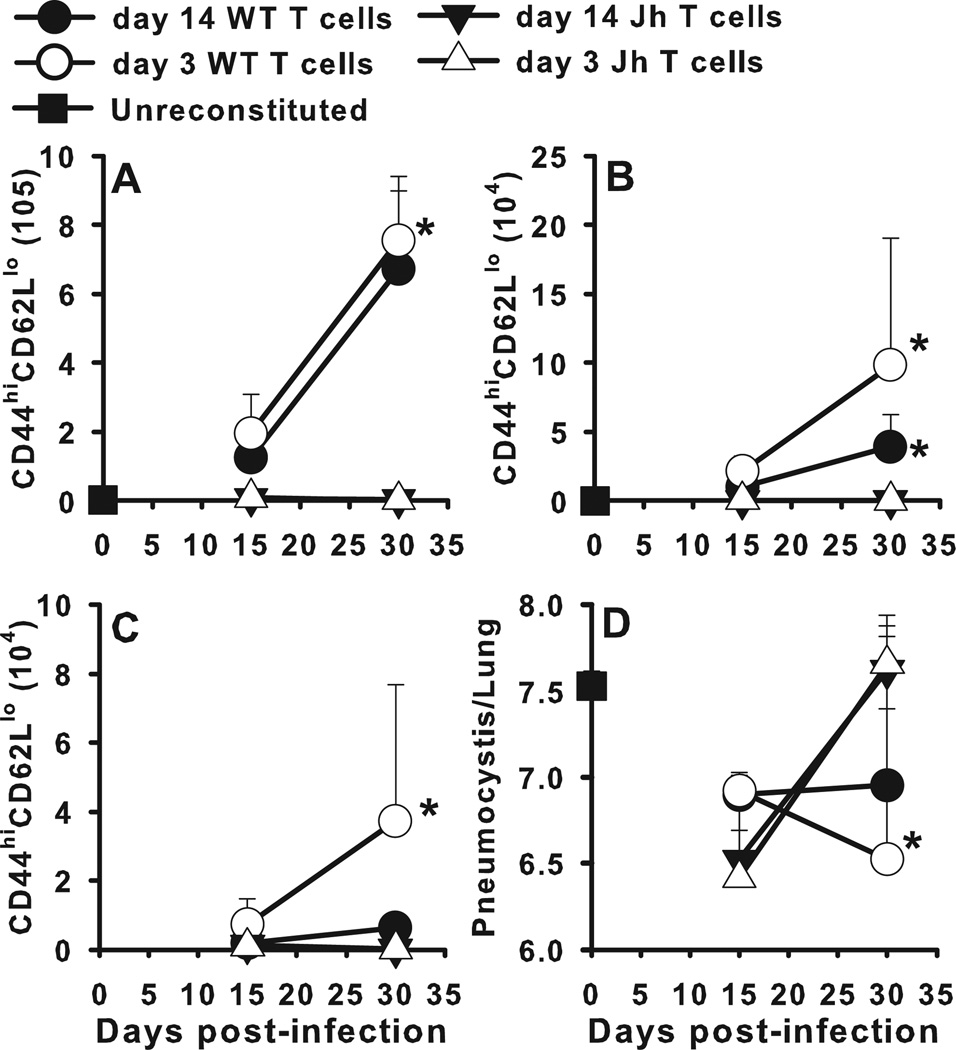
FIGURE 6.
CD4+ T cells primed for 3 days in B cell sufficient donors are capable of affecting clearance of PC in adoptive Rag−/− hosts. Donor wild type BALB/c or B cell-deficient Jh−/− mice were infected with PC and CD4+ T cells were isolated from the draining TBLN at 3 or 14 days post-infection. T cells were adoptively transferred into Rag−/− recipients followed by infection with PC nuclei 4 days later. T cells were identified by CD4, CD44, and CD62L staining using flow cytometry, with the number of activated CD4+ T cells (CD44hiCD62Llo) depicted over time in the (A) lung digest, (B) BALF, and (C) TBLN. (D) PC lung burden was assessed in lung digest samples and expressed as Log10 PC organisms per lung. Data are presented as mean ± SD for groups of 4 mice per timepoint per group and representative of 3 replicated experiments. Statistical significance defined at a p-value of < 0.05 for data generated in the Jh−/− recipients compared to recipients of T cells from WT mice at each timepoint (*).