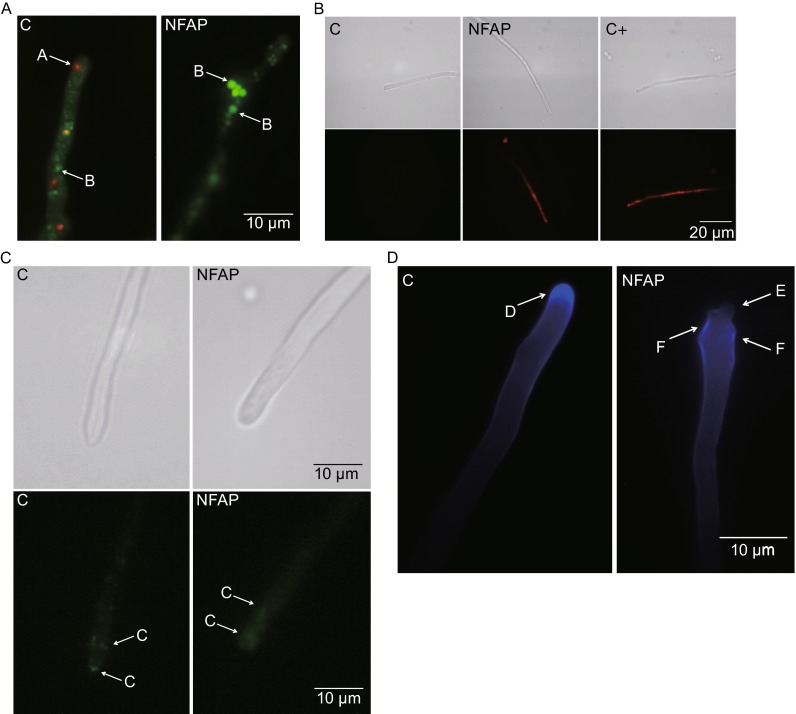
Figure 1.
Physiological changes in Aspergillus nidulans in the presence of Neosartorya fischeri antifungal protein (NFAP). (A) Viability staining of Aspergillus nidulans FGSC A4 hyphae with FUN-1 dye after NFAP treatment for 30 min at 37°C. Red vacuoles A indicates metabolic activity, while green vacuoles B metabolic inactivity. (B) Propidium iodide (PI) staining of A. nidulans FGSC A4 hyphae after NFAP treatment for 16 h at 37°C. Intracellular red fluorescence indicates membrane disruption. (C) Actin distribution at A. nidulans Actin-GFP hyphal tips in response to NFAP treatment for 30 min at 30°C. C: actin patch. (D) Calcofluor white (CFW) staining of A. nidulans FGSC A4 hyphae after NFAP treatment for 30 min at 37°C. D: cap-like CFW fluorescence - site of the chitin assembly, E: lack of the cap-like CFW fluorescence, F: delocalized chitin deposition. C: untreated control, C + : positive PI staining control-hypha was treated with 70% Et-OH for 1 h at 4°C, NFAP: NFAP-treated (25 µg/mL) hyphae. Upper images, light microscopy; lower images, fluorescence microscopy of PI staining (B) and of actin distribution (C)