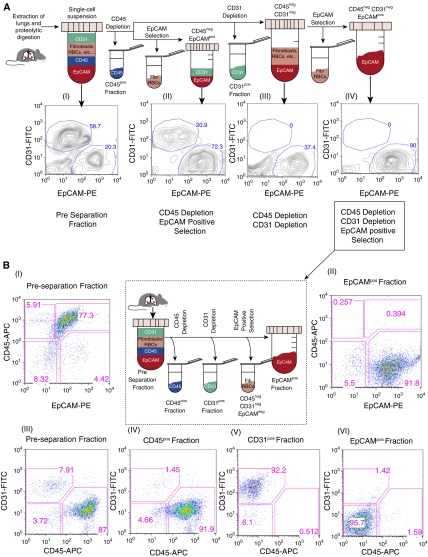
Figure 1.
Optimization of the magnetic-activated cell sorting (MACS) protocol for isolating lung epithelial, endothelial, and immune cells. (A) Flow cytometry analysis of single-cell suspensions from the lungs of a tumor-bearing Clara cell secretory protein (CCSP)–reverse tetracycline transactivator (rtTA) (+) tetracycline-responsive element (TetO) EGFRL858R (+) mouse (A [I]) before performing MACS-based separations. The whole single-cell suspension was then depleted of CD45pos cells, followed either directly by epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM)–positive selection (A [II]) or CD31 depletion (A [III and IV]). EpCAM-positive selection was then performed on a subset of the CD45negCD31neg cells (A [IV]). The highest epithelial cell purity was achieved using the latter protocol. All the fractions analyzed were gated on CD45neg cells. (B) Flow-based analysis of the EpCAMpos, CD31pos, and CD45pos fractions (B [II, IV–VI]) isolated using sequential CD45, CD31, and EpCAM selection (see center panel) compared with the preseparation fraction (B [I and III]). Flow analysis was performed on a FACSCalibur using CD31-fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC), CD45-allophycocyanin (APC), and EpCAM-phycoerythrin (PE) antibodies. EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; Fib, fibroblasts; RBC, red blood cell.