Figure 1.
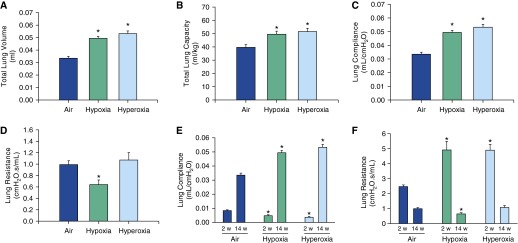
Lung function in adult mice exposed to air, hypoxia, or hyperoxia in the newborn period. Total lung volume (A), total lung capacity (B), and lung compliance (C) were increased in both hypoxia- and hyperoxia-exposed mice. Total lung resistance (D) was decreased in hypoxia-exposed mice. Compliance was lower at 2 weeks of age immediately after the exposure and higher at 14 weeks after the exposure (E) in both hypoxia- and hyperoxia-exposed groups compared with the air controls. Total lung resistance at 2 weeks after the exposure was higher in both hypoxia- and hyperoxia-exposed groups and lower in hypoxia-exposed mice 14 weeks after the exposure (F) (n = 6 per group; means ± SE). *P < 0.05 versus corresponding air group.
