Figure 4.
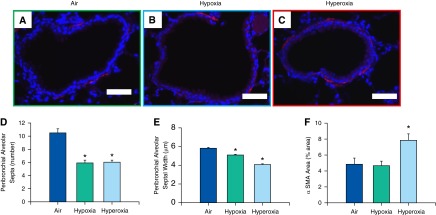
Analysis of bronchial α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) content and peribronchial alveolar septa assessment in adult mice exposed to air, hypoxia, or hyperoxia in the newborn period. (A–C) Representative photomicrographs of nonenzymatic fluorescent Cy-3 α-SMA–stained lung sections of adult mice exposed to air (A), hypoxia (B), or hyperoxia (C) in the newborn period (400×; calibration bars, 50 μm). Number of septa attached per bronchus (D) and their thickness (E) were reduced in both hypoxia- and hyperoxia-exposed mice (n = 18, 6 per group; means ± SE). *P < 0.05 versus corresponding air group. Percentage of total area occupied by α-SMA was increased in adult mice exposed to neonatal hyperoxia (F) (n = 6 per group; means ± SE). *P < 0.05 versus corresponding air group.
