Figure 6.
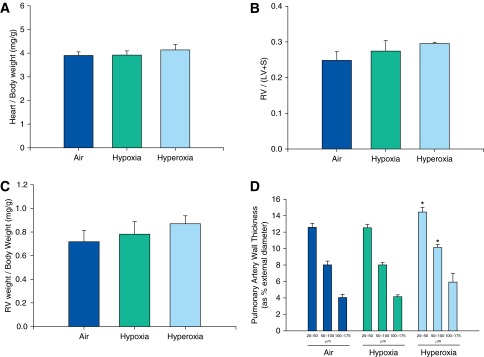
Analysis of cardiac and pulmonary arterial remodeling of adult mice exposed to air, hypoxia, or hyperoxia in the newborn period. Ratios of heart to body weight (A), RV weight per LV plus septum (S) weight (B), and RV weight per body weight (C) were not significantly different among adult mice exposed to air, hypoxia, or hyperoxia in the newborn period. Pulmonary arterial wall thickness in small arteries (20–50 μm and 50–100 μm) was increased in adult mice exposed to neonatal hyperoxia compared with air controls (D) (n = 6 per group). Data presented are means ± SE. *P < 0.05 versus corresponding air group.
