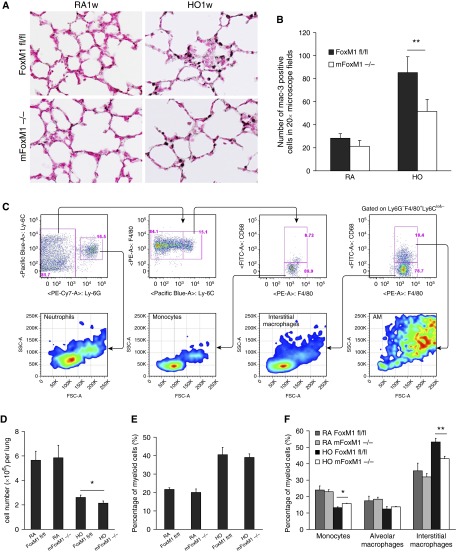
Figure 4.
Foxm1 deletion from myeloid cell lineages decreases accumulation of pulmonary interstitial macrophages after prolonged postnatal hyperoxia. Newborn mFoxm1−/− and control Foxm1fl/fl mice were exposed to HO or RA and harvested at 3 weeks of age. (A and B) Immunostaining for Mac-3 showed reduced numbers of macrophages in HO-exposed mFoxm1−/− lungs. The number of Mac-3–positive cells was counted in 10 random sections using five mice in each group. Original magnification: ×400. **P < 0.05. (C) Inflammatory cells were isolated from lung tissue of mFoxm1−/− or Foxm1fl/fl mice after 1 week of HO-exposure. Dead cells were excluded using 7-aminoactinomycin stain. The following cell surface markers were used to identify cell types: neutrophils, CD45+CD11b+Ly6C+ Ly6G+; monocytes, CD45+CD11b+ Ly6ChiLy6G−F4/80+; interstitial macrophages, CD45+CD11b+ Ly6C−Ly6G− F4/80+CD68−; alveolar macrophages, CD45+CD11b+ Ly6C−Ly6G− F4/80+CD68+. (D) HO-exposed mFoxm1−/− mice had a lower total cell count than Foxm1fl/fl mice. (E) The percentage of myeloid cells was calculated by flow cytometry using CD45+CD11b+ cell surface markers. Although the percentage of myeloid cells increased significantly after HO exposure, there were no significant differences between mFoxm1−/− and Foxm1fl/fl mice. (F) Decreased numbers of interstitial macrophages were observed in HO-exposed mFoxm1−/− lungs. Cell numbers were counted after enzymatic digestion of lung tissue (n = 5 mice per group).The percentage of interstitial macrophages was decreased in HO-exposed mFoxm1−/− lungs, whereas the number of alveolar macrophages was unaltered. The number of monocytes was increased in HO-exposed mFoxm1−/− lungs compared with controls. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. FSC-A, forward scatter defined by area; PE-A, intensity of phycoerythrin-stained cells defined by area; SSC-A, side scatter defined by area.