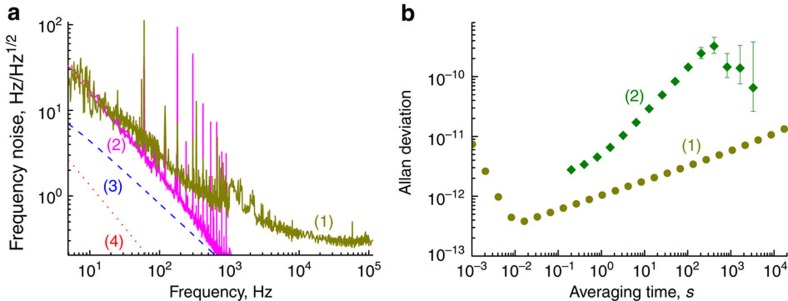
Figure 3. Spectral purity and stability characteristics of the laser.
(a) Linear frequency noise of the RF beat note of the lasers, (1) compared with the noise determined by conversion of the laser power fluctuations to the frequency fluctuations, (2) as well as fundamental thermorefractive, (3) and thermoexpansive (4) noise. (b) Allan deviation interpolated using the frequency noise data (1) and actual measurement of the Allan deviation (2). The 500-s peak in curve (2) results from the air conditioner cycle in the laboratory. This systematic frequency shift exceeds the internal laser noise rather significantly.