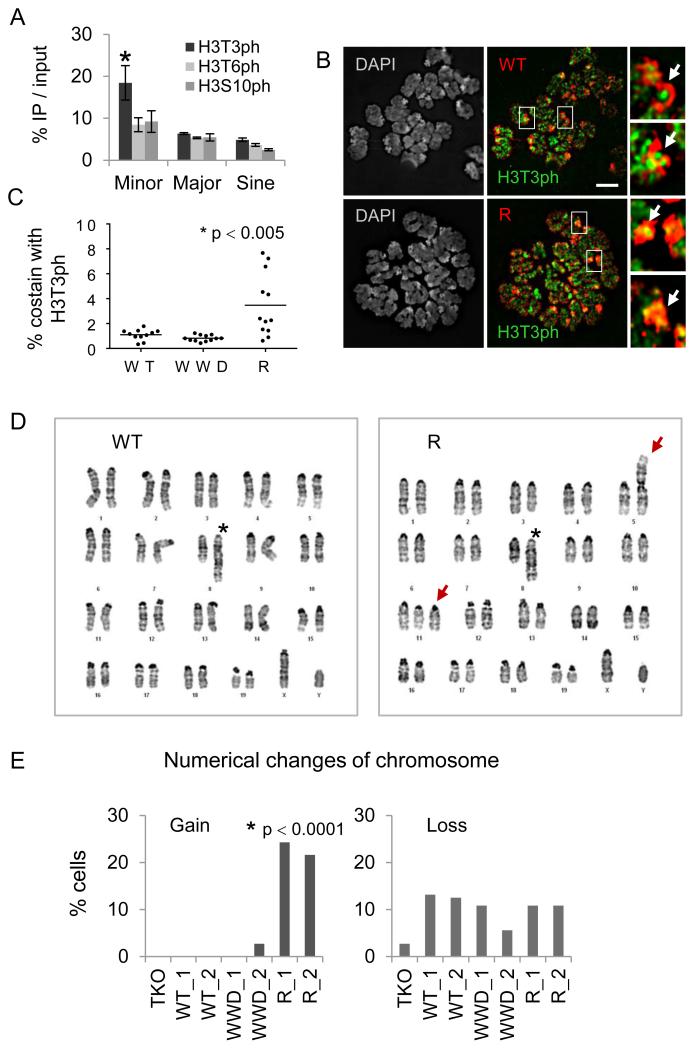
Figure 6.
The R-Dnmt3a2 mutant insensitive to mitotic H3T3ph causes chromosomal abnormalities.
A, ChIP-qPCR of H3T3ph, H3T6ph, and H3S10ph signals in repeat regions. Error bars represent s.e.m. of three experiments, *p < 0.05. B, Immunofluorescence of metaphase chromosomes reacted with antibodies against H3T3ph (green) and FLAG-tagged WT- or R-Dnmt3a2 (red). Arrows indicate pericentromeric and centromeric regions. Scale bar, 5 μm. C, Quantification of FLAG signal colocalized with H3T3ph at DAPI-dense regions (counts are based on 11~12 metaphase cells in individual clones). D, Representative karyotype images of WT- or R-Dnmt3a2-expressing ESCs. Asterisks in left “WT” and in right “R” mark a partial duplication on chromosome 8. Arrows in right “R” indicate Robertsonian fusion on chromosome 5 and trisomies on chromosome 11. E, Changes in chromosome numbers in ESCs expressing WT-, WWD-, or R-Dnmt3a2 (counts are based on 36~40 metaphase cells in individual clones). *p < 0.0001, Pearson’s Chi-squared test.