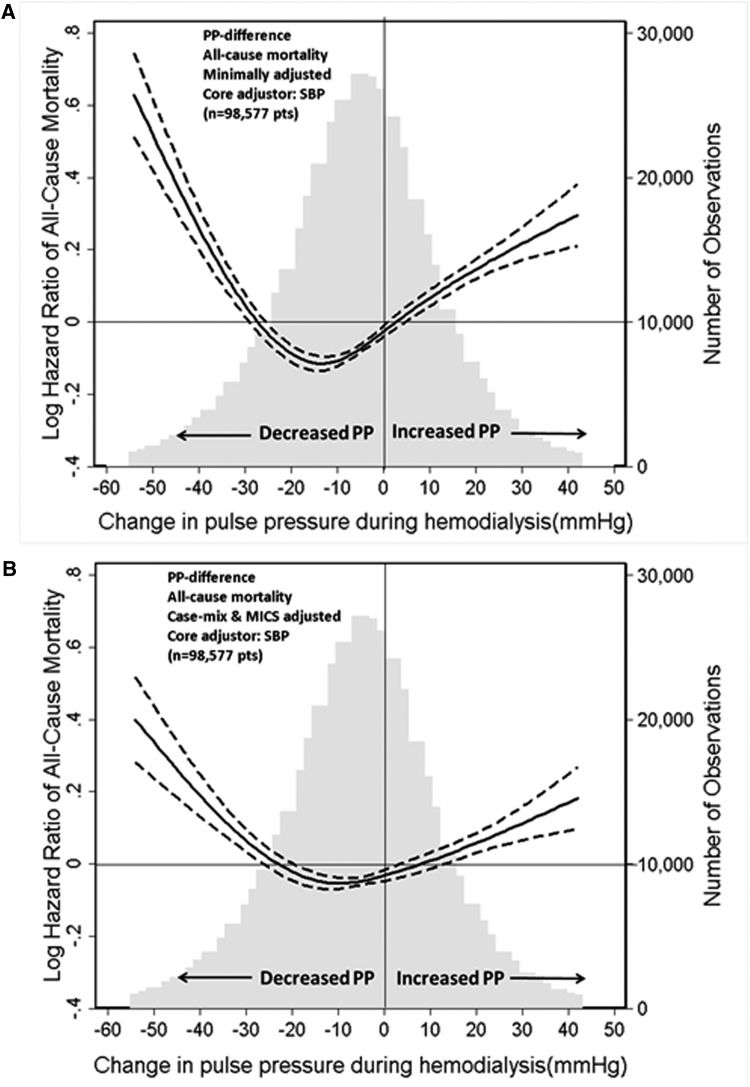
Figure 1.
SBP-adjusted hazard ratio for the association between change in pulse pressure during hemodialysis and all-cause mortality. Minimally SBP-adjusted model (A) and SBP plus case-mix plus MICS-adjusted model (B). Dashed lines represent 95% confidence interval. Change in PP was defined as postdialysis PP minus predialysis PP. Minimally SBP-adjusted model included adjustment for entry calendar quarter and predialysis SBP. SBP plus case mix plus MICS-adjusted model included covariates in the minimally SBP-adjusted model plus age, sex, race/ethnicity, presence of diabetes mellitus, nine preexisting comorbidities, history of tobacco smoking, dialysis duration categories, primary insurance, types of vascular access, dialysis dose as indicated by single pool Kt/V, ultrafiltration percentage, body mass index, serum levels of albumin, creatinine, total iron-binding capacity, ferritin, calcium, phosphorus, bicarbonate, hemoglobin, blood white blood cells, and lymphocyte percentage. MICS, malnutrition-inflammation complex syndrome; PP, pulse pressure; SBP, systolic BP.