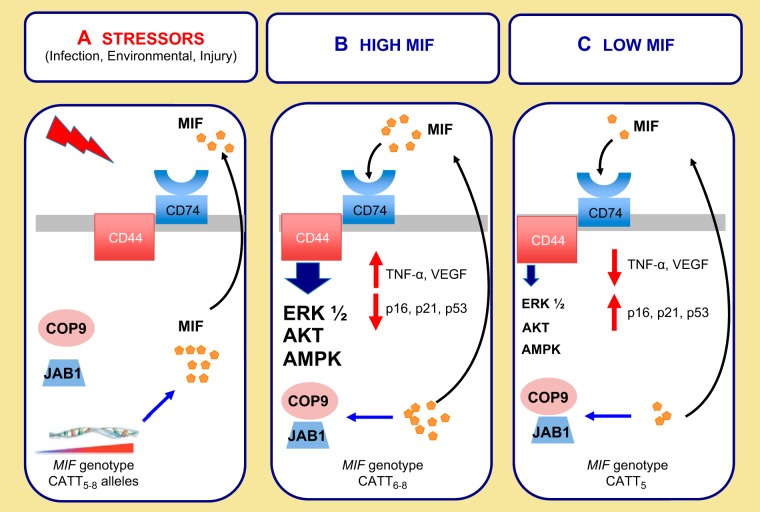
Fig. 1.
A: in response to diverse biological stressors, macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) is secreted from preformed intracytoplasmic pools. Subsequently there is an increase in MIF gene transcription. A CATT microsatellite repeat in the promoter region influences gene transcription. B: MIF can signal through its receptor CD74 and coreceptor CD44 to activate ERK 1/2 AKT and AMPK signaling pathways or via an intracellular JAB1 pathway. High MIF conditions result in the transcription of proinflammatory and angiogenic mediators such as TNF-α and VEGF. MIF is also a key cell cycle regulator and can suppress p53- and p16-mediated apoptosis and/or cellular senescence. High-expressing CATT6–8 alleles correspond to increased MIF gene expression. C: the CATT5 allele is associated with decreased transcription of MIF. Low MIF states result in relatively decreased transcription of proinflammatory and angiogenic mediators and a relatively increased susceptibility to apoptosis and cellular senescence.