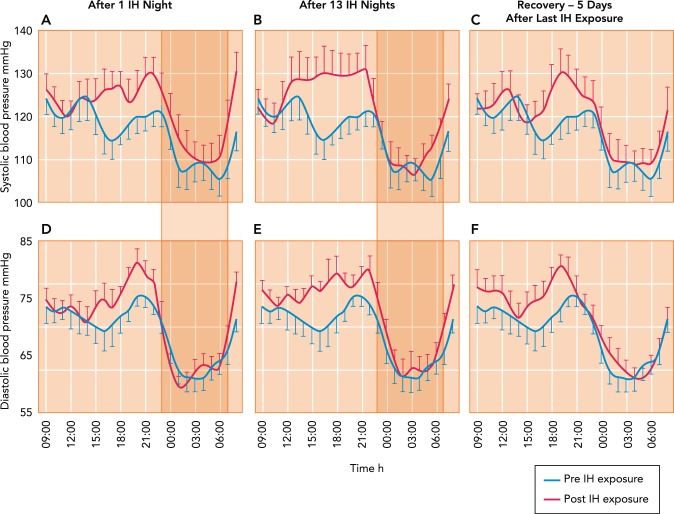
FIGURE 6.
Effects on ambulatory systemic blood pressure of nocturnal intermittent, oscillating hypoxemia
Hour-by-hour effects on ambulatory systemic blood pressure of nocturnal intermittent, oscillating hypoxemia consisting of 8 h of daily of oscillatory poikilocapnic hypoxia (FiO2 of 0.13 every 105 s alternated with 15 s of FiO2 of 1.0, producing periodic swings of SpO2 of ∼88–98%) in healthy young adults. Note that increases in blood pressure resulting from IH occurred 1) just before waking (5–7 AM), then returned to normal until increasing again over the late afternoon and evening; 2) during the daytime hours after 1 night of IH, and increased further after 13 IH nights; and 3) returned to normal after 5 nights in normoxia. The IH effects on daytime BP were accompanied by significant increases in MSNA burst frequency and reductions in baroreceptor sensitivity. Figure was reproduced from Ref. 116 with permission from the European Respiratory Society.