FIGURE 2.
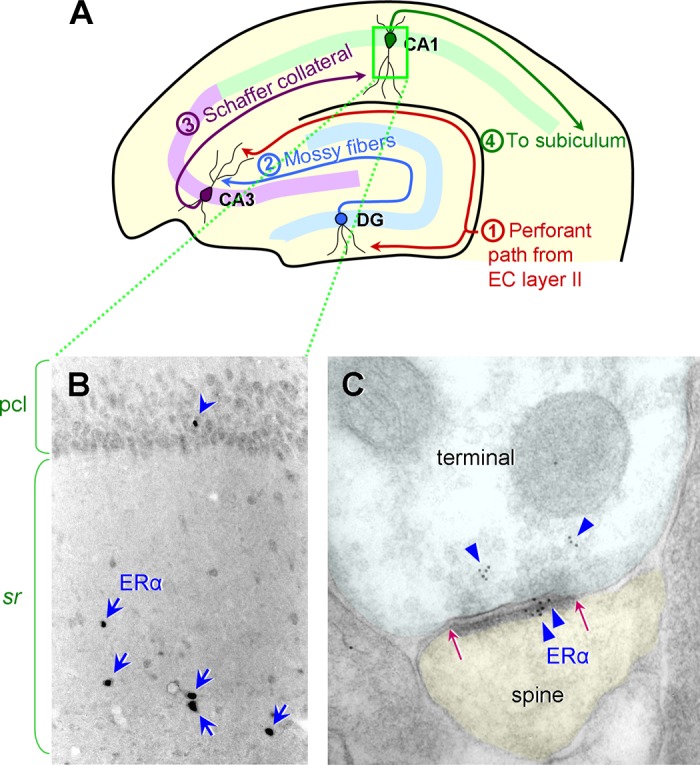
ER α expression in the rat and monkey hippocampal CA1. A: a schematic diagram illustrating the hippocampal circuit and the major inputs to and outputs from the dentate gyrus (DG), CA3, and CA1. The perforant path from the entorhinal cortex (EC) layer II projects to the DG middle/outer molecular layers and the CA3 stratum lacunosum/moleculare. The DG granule cells project to the CA3 stratum lucidum via the mossy fiber tract. The CA3 pyramidal neurons project to the CA1 stratum radiatum and oriens via the Schaffer collaterals. The CA1 pyramidal neurons project to the subiculum. [Diagram modified from Hara and Morrison (68).] B: in the rat CA1, a few interneurons with cell nuclear ER α are found primarily in the stratum radiatum (sr), indicated by blue arrows. Nuclear ER α is less frequently found in the pyramidal cell layer (pcl; blue arrowhead). [Adapted from Milner et al. (140).] C: similar to rodents, rhesus monkeys express abundant ER α in the CA1. ER α immunogold particles (blue triangles) are present in both the presynaptic terminal and the postsynaptic spine. Postsynaptic ER α labeling is concentrated within the postsynaptic density (PSD), the extent of which is indicated by red arrows. [Electron micrograph adapted from Wang et al. (223).]
