FIGURE 46.
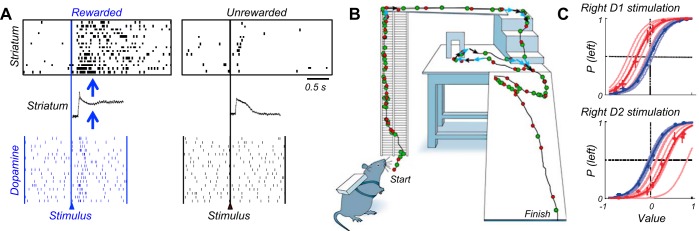
Immediate dopamine influences. A: hypothetical mechanism of influence of dopamine reward signal on striatal reward response. Bottom: a rewarded, but not unrewarded, stimulus differentially activates a dopamine neuron. [From Tobler et al. (598).] Middle: possible dopamine influence on striatal synaptic potentials: dopamine D1 receptor agonist prolongs the depolarization of a striatal neuron. [From Hernández-Lopez et al. (213).] Top: as a result of the dopamine influence on striatal depolarization, the striatal neuron responds stronger to a rewarded compared with an unrewarded stimulus. [From Hollerman et al. (222).] B: influence of dopamine reward signal on behavioral navigation. Electrical stimulation to the left and right somatosensory cortex of rats provides cues for turning; electrical stimulation of the medial forebrain bundle containing dopamine axons induces forward locomotion. The combined stimulation is able to guide a rat through a three-dimensional obstacle course, including an unnatural open field ramp. Colored dots indicate stimulation of forebrain bundle and somatosensory cortex. [From Talwar et al. (580). Reprinted with permission from Nature Publishing Group.] C: influence of dopamine reward signal on behavioral choices. Unilateral optogenetic stimulation of mouse striatal neurons expressing dopamine D1 or D2 receptors induces immediate differential choice biases (left bias for right D1 stimulation, top; and right bias for right D2 stimulation, bottom). [From Tai et al. (576). Reprinted with permission from Nature Publishing Group.]
