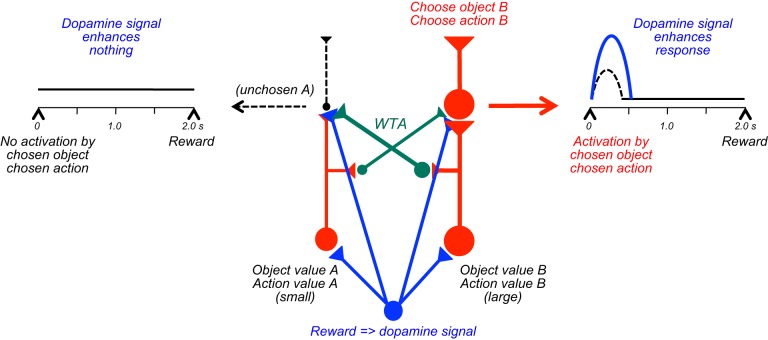
FIGURE 47.
Hypothetical mechanism of immediate dopamine influence on neuronal coding of decision variables. For the basic competitive decision mechanism, the dopamine signal arises from a temporal difference (TD) prediction error in chosen value at the time of the decision. The dopamine signal boosts differences in activity between the two options reflecting object value or action value (bottom). Alternatively, and more effectively, the signal may enhance activities representing chosen object or chosen action selected by the winner-take-all (WTA) mechanism (top right), while leaving nonexisting activity unchanged (top left). The weight of dots and lines in the circuit model indicates level of neuronal activity. Dotted lines indicate inputs from unchanged neuronal activities. Crossed green connections are inhibitory.