Figure 5.
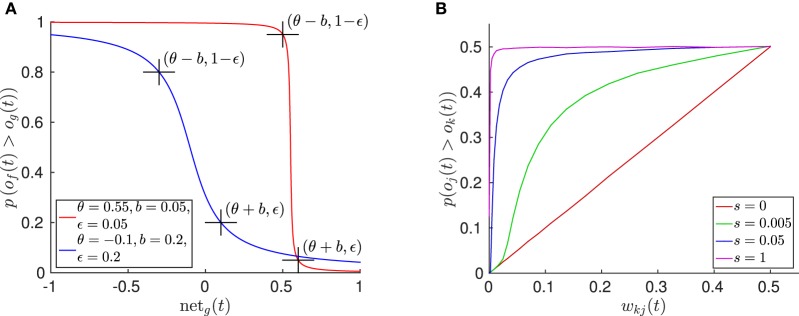
Properties of the spatial and temporal pattern learning algorithm. (A) Plot of the cumulative pattern recruitment probability for two exemplar function parameterizations. Here, og(t) denotes the activation of the best matching, trained pattern, and of(t) denotes the activation of the free pattern. (B) Plot of the effect caused by temporal pattern learning, yielding temporally predictive, lateral inhibition between pattern neurons. Here the inhibition effect of pattern neuron k on pattern neuron j is illustrated, which is determined by wkj. The relative pattern winning probability of j over k depends on the signal strength s, given that both neurons are randomly activated with equal strength on average. The plot shows the result of 500 k randomly sampled trials per measuring point of wkj and s, in which both neural activations were set uniformly randomly to ok(t) ϵ [−1, 1] · s and oj(t) ϵ [−1, 1] · s. The result shows that with increasing signal strength the influence of the lateral bias decreases, while the lateral inhibition nearly fully determines the transition probability given a very weak signal.
