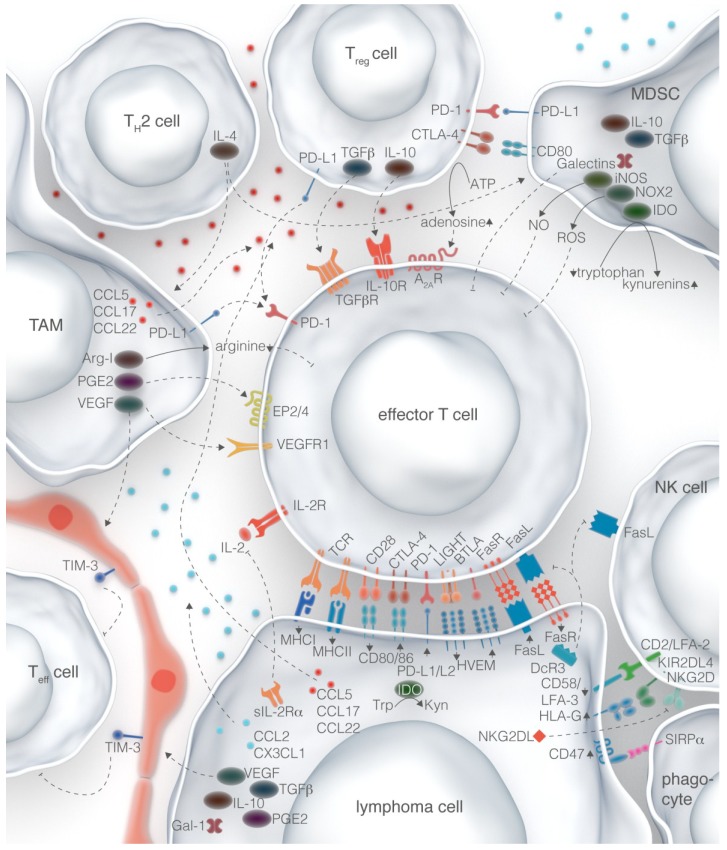
Figure 1.
Immune evasion mechanisms in the lymphoma microenvironment. Lymphoma cells can suppress anti-tumor immune cells (e.g., effector T cells, NK cells, and phagocytes) directly through surface-mediated mechanisms as well as secreted factors. Chemokines expressed by the lymphoma cell can also recruit regulatory cells (e.g., tumor-associated macrophages, myeloid-derived suppressor cells, Tregs, and Th2-polarized cells) that form a complex network of interactions to maintain a tolerogenic microenvironment and allow the lymphoma cell to escape detection.