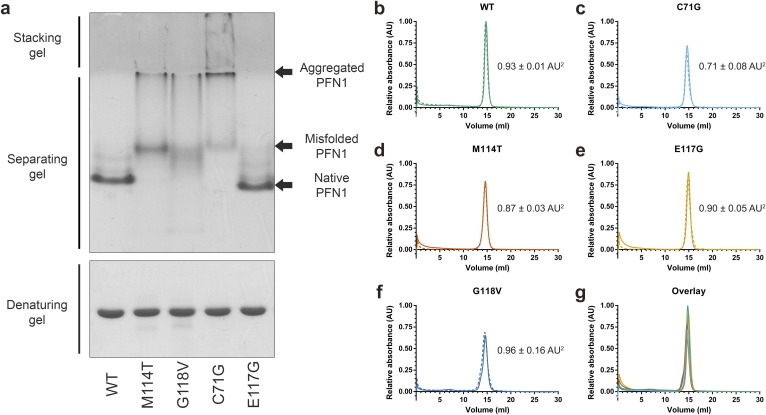
Fig. S5.
Analysis of PFN1 proteins by native page and analytical size-exclusion chromatography. (A) PFN1 proteins (10 μg) were subjected to native (Top) or denaturing (Bottom) gel electrophoresis and detected with Coomassie Brilliant Blue stain. The mobility of native PFN1 WT is indicated. PFN1 E117G migrates with a slightly faster mobility than PFN1 WT owing to the addition of a negatively charged amino acid. Misfolded ALS-linked PFN1 variants migrate with slower mobility and form aggregated species that are retained in the stacking gel. This gel is representative of n = 2 experiments using proteins from different purification preparations. (B–F) The indicated PFN1 protein (40 μg) was subjected to analytical size-exclusion chromatography using a Superdex 75 column. A single peak corresponding to the expected elution volume (∼15 mL) for monomeric PFN1 was detected for all PFN1 proteins. The experiments were carried out in duplicate for each variant, indicated by solid (n = 1 experiment) and dashed (n = 2 experiment) lines. The average relative peak area ± the SD is indicated to the right of each curve. Despite equal sample loading, the peak area of PFN1 C71G and M114T is lower than that of WT (within error), consistent with a reduced level of soluble protein for these ALS-linked variants. (G) An overlay of B–F for the n = 1 experiment demonstrates a similar elution profile for all PFN1 proteins.