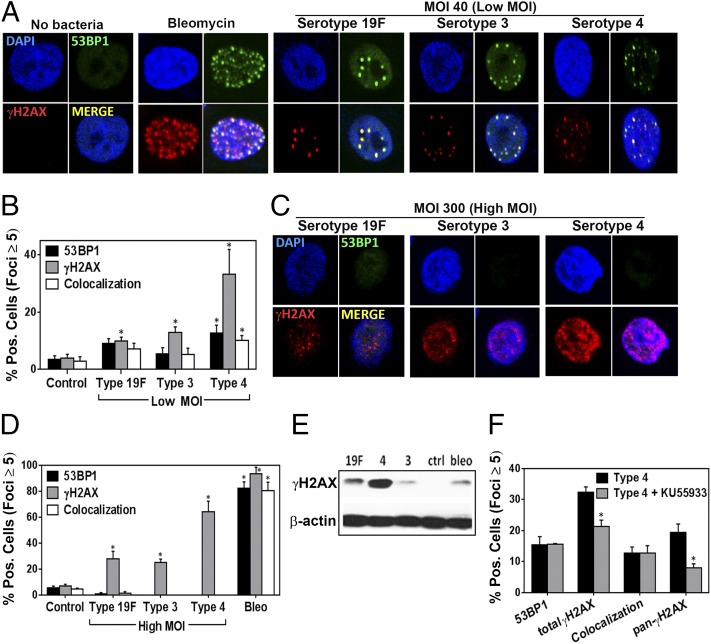
Fig. 1.
S. pneumoniae induces DNA damage in human alveolar (A549) cells in the form of DSBs. (A) Representative images of alveolar epithelial cells showing DSBs (indicated by γH2AX and 53BP1 foci) after exposure to S. pneumoniae serotypes 19F, 3, and 4 for 7 h at MOI 40 (Low MOI). Bleomycin (100 μM) serves as a positive control. (B) γH2AX- and 53BP1-positive cells (≥5 foci per nucleus) were quantified for each condition and expressed as percentage positive. (C–E) Alveolar epithelial cells were exposed to serotypes 19F, 3, and 4 at MOI 200–400 (High MOI). (C) Representative images of alveolar epithelial cells after exposure to S. pneumoniae at MOI 300. (D) γH2AX- and 53BP1-positive cells were quantified for each condition. (E) The alveolar epithelial cells were also lysed and analyzed by Western for γH2AX. (F) Alveolar epithelial cells were pretreated with ATM inhibitor KU55933 (20 μM for 2 h) and then exposed to serotype 4 (type 4) at MOI 40 for 7 h. γH2AX-positive cells were quantified for each condition. For B and D, each data point represents mean ± SEM for four experiments. For F, each data point represents mean ± SEM for three experiments. For B, D, and F, *P < 0.05, unpaired Student’s t test.