Figure 1.
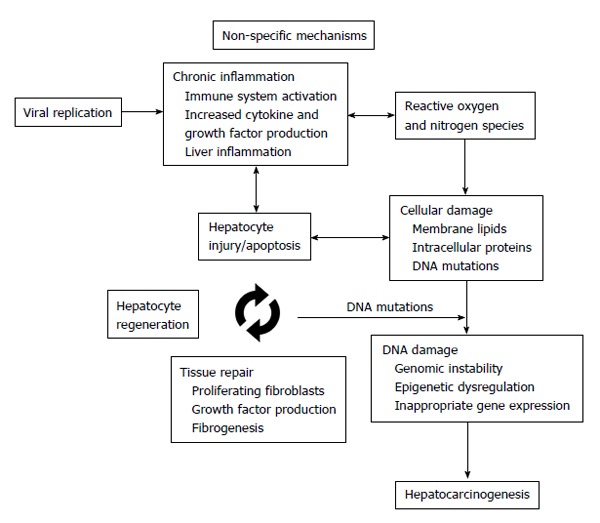
Chronic inflammation in the liver is characterized by sustained damage leading to hepatocyte death/regeneration and tissue repair cycle. Activation of inflammatory signaling with increased cytokine and growth factor production leads to oxidative stress which contributes to cellular damage. Cumulative damage to cellular structures, proteins and chromosomes alters genomic and epigenomic functions which can eventually induce hepatocarcinogenesis.
