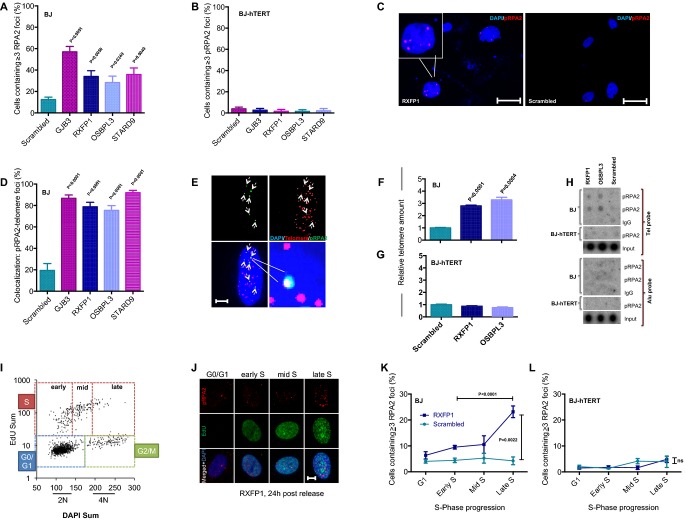
Figure 3.
Telomerase rescues aneuploidy-induced replication stress
- A–C Analysis of phosphorylated RPA2 (pRPA2) foci by immunofluorescence staining: quantification of nuclear pRPA2 foci in (A) BJ and (B) BJ-hTERT fibroblasts; (C) representative images of pRPA2 foci (scale bar: 50 μm). Note that telomerase expression completely suppresses the induction of pRPA2 foci in BJ fibroblasts infected with aneuploidy-inducing shRNAs (B).
- D Co-staining of pRPA2 foci and telomeric DNA by FISH was used to quantify the number of pRPA2 foci co-localizing to telomeres in cells infected with aneuploidy-inducing shRNAs compared to scrambled shRNA-infected cells.
- E Representative image of immuno-FISH shows co-localization of pRPA2 foci and telomeric DNA. Here, 5 of 6 pRPA2 foci (dashed arrows) co-localize with telomeres (scale bar: 10 μm).
- F–H Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) was carried out using a pRPA2 antibody on lysates of cells infected with aneuploidy-inducing shRNAs or scrambled shRNA control. qPCR-based quantification of telomeric DNA in the immunoprecipitate of (F) BJ and (G) BJ-hTERT cells. (H) Quantification of telomeric DNA (telomere probe) and non-telomeric DNA (Alu probe) in the immunoprecipitate by dot blot and radioactive labeling. IgG-ChIP was used as a negative control. Note that aneuploidy-inducing shRNAs induced pRPA2 binding at telomeric DNA, which was rescued by telomerase expression. There was no detectable increase in pRPA2 foci at chromosomal localizations outside telomeres.
- I–L Quantification of cell cycle-dependent accumulation of pRPA2 foci formation in BJ cell infected with an aneuploidy-inducing shRNA against RXFP1 or with a scrambled shRNA control. Serum-starved, G1-arrested cells were re-stimulated and labeled at different time points with EdU. (I) Representative 2D cell cycle profile (EdU versus DAPI) at 24 h post-release from serum starvation. (J) Representative pictures of pRPA2 staining at the indicated cell cycle stages (scale bar: 10 μm). Quantification of pRPA2 foci at the indicated cell cycle stages in shRNA RXFP1- and scrambled shRNA-infected (K) BJ and (L) BJ-hTERT cells. Note the significant increase in pRPA2 foci in shRNA RXFP1-infected cells in late S-phase.
Data information: (A, B, D) Mean ± SEM, two-tailed t-test, n ≥ 50 cells per sample. (F, G) Mean ± SEM, two-tailed t-test, n = 3 replicates. (K, L) Mean ± SEM, one-way ANOVA + Tukey’s test, n = 3–7 replicates.
Source data are available online for this figure.