Figure 2.
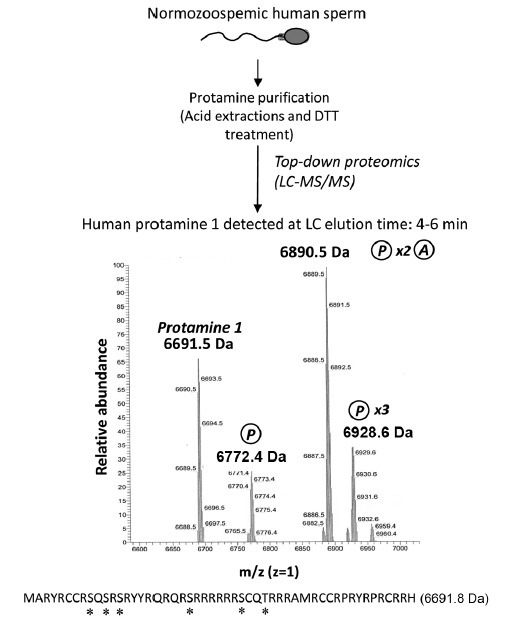
Analysis of the intact human sperm protamine sequences by MS. After following the indicated workflow and LC-MS/MS analysis, the registers obtained demonstrate the presence of the intact unmodified Protamine 1 mass and masses of the protamine 1 containing different combinations of phosphorylation and acetylation. Methods: human sperm cells from normozoospermic sperm donors were collected and processed as described92 following World Health Organization guidelines125 and in accordance with the ethical and internal review board guidelines. Seminal plasma was discarded and sperm were treated with acid and reducing agents,92 in order to obtain a protein extract constituted mostly by a mixture of purified protamine 1 (P1) and protamine 2 (P2) (top). The correct protamine purification was confirmed through acid-urea polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, as previously described,61 prior to the analysis by LC-MS/MS. Spectra corresponding to the liquid chromatography elution time 4–6 min obtained after MS analysis of nondigested proteins (top-down proteomics) is shown in the middle of the image. Mass peaks corresponding to nonmodified P1, mono-phosphorylated P1, di-phosphorylated and mono-acetylated P1, and tri-phosphorylated P1 were observed (note that each peak is showing a mass/charge (m/z) value corresponding to a specific “m,” since “z” is set as 1). A maximum error of 200 ppm between theoretical and experimental masses was considered to give a match as valid. At the bottom of the figure, the human P1 amino-acid sequence is indicated together with its theoretical “m.” Potential phosphorylation and acetylation sites are highlighted with an asterisk. DTT: dithiothreitol; MS: mass spectrometry; LC-MS/MS: liquid chromatography followed by tandem mass spectrometry.
