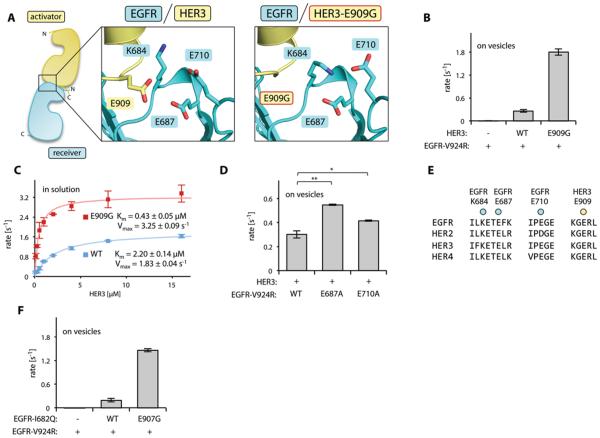
Figure 6.
Effect of the E909G mutation on the allosteric activator function of HER3. (A) Diagram showing the cluster of charged residues in the vicinity of HER3 Glu909 at the activator/receiver interface of the EGFR/HER3 dimer (left) and in the EGFR/HER3-E909G dimer (right). (B) Activity of the EGFR-V924R kinase domain in the presence of the indicated HER3 kinase domain constructs in the vesicle-based assay. (C) Activity of the EGFR-V924R kinase domain upon titration with the wild-type (WT, blue) or E909G (red) HER3 kinase domain. Both EGFR and HER3 contained the kinase domains and the full JM segments. (D) The activity of the EGFR-V924R kinase domain without additional mutation (WT) or with the indicated mutation in the presence of the wild-type HER3 kinase domain in the vesicle-based assay. (E) Sequence conservation of amino acid residues in the acidic cluster surrounding Glu909. (F) Activity of the EGFR-V924R kinase domain in the presence of the HERG1-I682Q kinase domain containing either no additional mutations (WT) or the E907G mutation in the vesicle-based assay. In panels B, C, D, and F, data are plotted as the mean and standard deviation of three independent experiments, *p<0.005, **p<0.001.