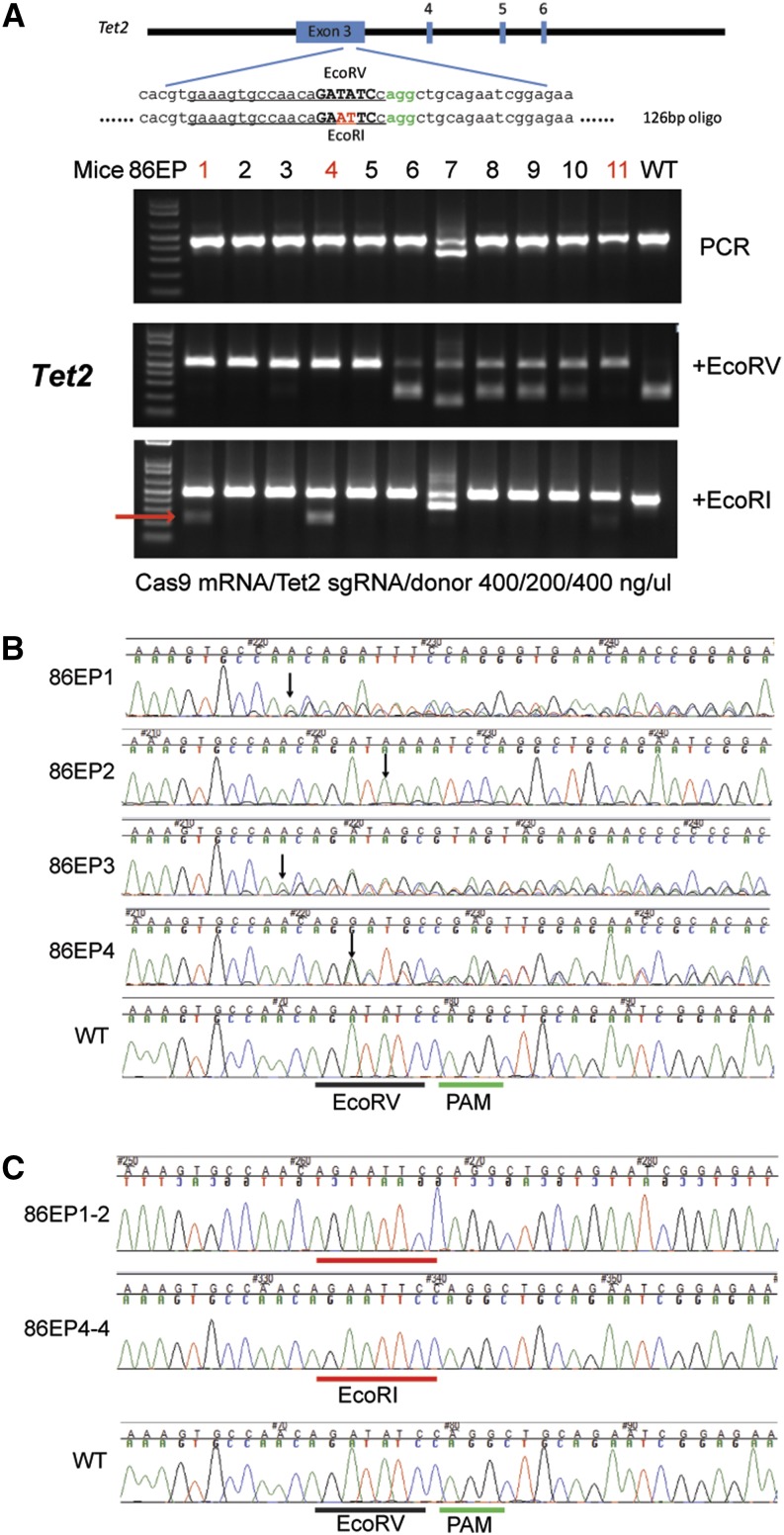
Figure 2.
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated HDR mutation in live mice delivered by electroporation. (A) Top panel, schematic of the target sequence and donor oligonucleotide from mouse Tet2 locus. The protospacer sequence is underlined and PAM sequence colored in green. Oligonucleotide-directed 2-bp changes are colored in red. Lower panel, RFLP analysis of 11 mice from the group electroporated with Cas9 mRNA, sgRNA targeting the Tet2 locus, and donor oligonucleotide at 400/200/400 ng/μl as indicated at the bottom of the panel. The cleaved band from the introduced EcoRI site is indicated by a red arrow. (B) Sequencing traces of PCR products encompassing the Tet2 target region from four mutant mice presented in A (86EP1–4). The PAM sequence is underlined by a green bar and the wild-type EcoRV site, a black bar. Overlapping sequencing traces among the mutant mice indicate existence of more than one allele among these mice, as compared to the WT mouse. The positions of the start of mutations are indicated by black arrows. (C) PCR products from two mice, 86EP1 and 86EP4, were cloned and individual clones sequenced. Sequences from clones 86EP1-2 and 86EP4-4 are shown. Precise modification converting EcoRV (underlined by a black bar) to EcoRI (underlined by a red bar) site was confirmed in these two mice.