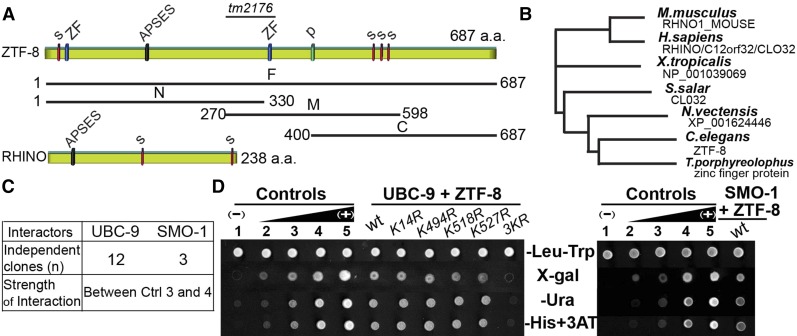
Figure 1.
ZTF-8 is a conserved protein that interacts with both UBC-9 and SMO-1. (A) Scheme of the C. elegans ZTF-8 protein and its human functional homolog, RHINO. The region deleted in the tm2176 mutant allele (codons 287–351) is indicated. Four predicted SUMOylation sites (s), two zinc-finger motifs (ZF), one APSES DNA binding site (APSES), and a phosphorylation site (p) are indicated. Full length (F) and truncations (N, M, C) of ZTF-8 used in a yeast two-hybrid screen are indicated. (B) Phylogenic tree comparing the potential orthologs of ZTF-8 with various species by ClustalW2 (EMBL-EBI). (C) Results from a yeast two-hybrid screen using the full-length and truncated versions of ZTF-8 as bait. The strength of the protein interaction is graded on the basis of comparison with one negative and four positive controls (as shown in D). (D) The yeast two-hybrid screen identified UBC-9 and SMO-1 as binding interactors for ZTF-8. Wild type as well as the indicated point mutants of ZTF-8 were tested for their interaction with UBC-9 (left) or SMO-1 (right). ZTF-8 fused to the DNA binding domain and the UBC-9/SMO-1 fused to the activation domain of GAL4 were analyzed in a yeast two-hybrid assay. One negative (no. 1) and four positive controls (nos. 2–5) were used as described in Walhout and Vidal (2001). Interactions were scored by growth on X-gal, SC–Ura, and SC–His +1 mM 3AT plates and compared to growth on the control SC–Let–Trp plates.