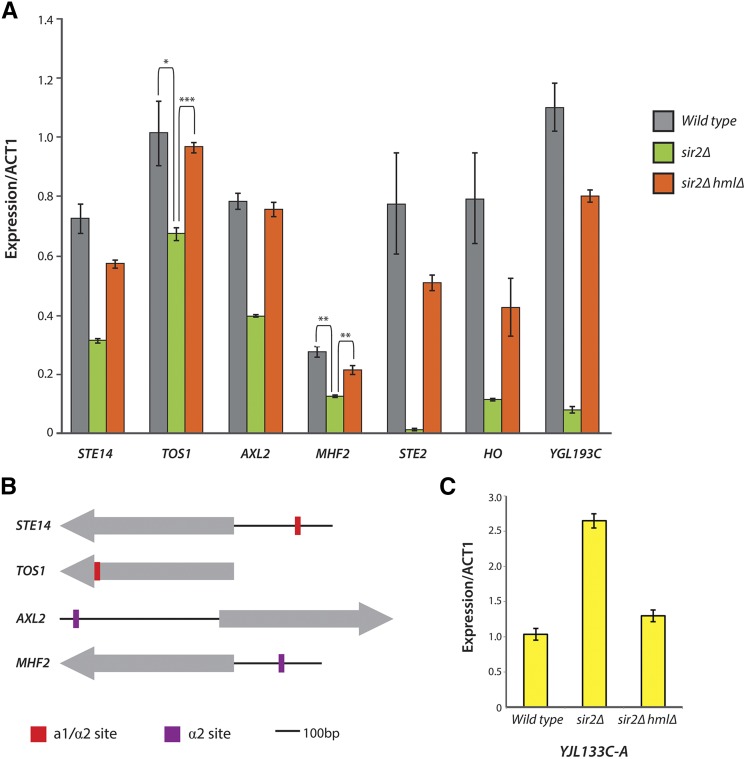
Figure 7.
Expression confirmation via qRT-PCR and promoter analysis of candidate haploid-specific genes. (A) STE14, TOS1, AXL2, and MHF2 were weakly repressed in an α2-dependent manner. The strongly a1/α2-repressed genes STE2, HO, and YGL193C are shown for comparison. (B) Annotated binding sites for the a1/α2 heterodimer and α2 itself are shown in relation to the protein-coding sequences (gray arrows) for STE14, TOS1, AXL2, and MHF2 (coding regions are not drawn to scale). STE14 contains a weak a1/α2 binding site 232 bp upstream from its coding sequence. TOS1 contains a weak a1/α2 binding site within its gene body. Both AXL2 and MHF2 contain weak α2 binding sites 578 and 174 bp, respectively, upstream from their coding regions. (C) YJL133C-A, a gene of unknown function, increases in expression in a α2-dependent manner.