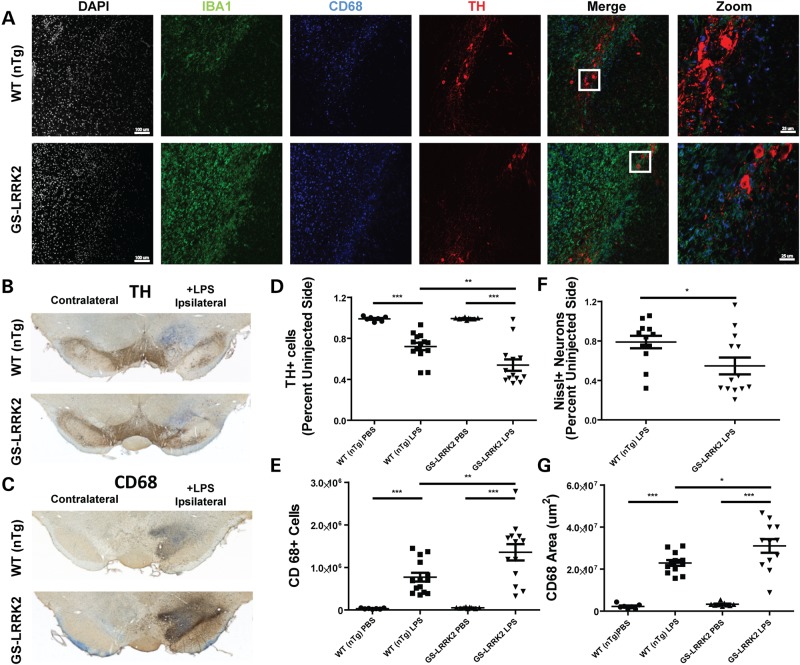
Figure 1.
Enhanced neuroinflammation in G2019S LRRK2 transgenic rats. 10- to 12-week-old non-transgenic littermate controls (WT nTg, n = 10) and G2019S LRRK2 (GS-LRRK2, n = 13) rats were unilaterally injected with 5 µg ultra-pure lipopolysaccharide (LPS) into the right substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc). Animals were sacrificed 2 weeks post-injection. (A) Representative confocal images of the SNpc stained for ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1 (IBA1) and cluster of differentiation protein 68 (CD68), both markers of myeloid cells, along with tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) expressed in dopaminergic neurons. White boxes in the merge panels represent the area for ‘Zoom’ panels. Scale bars for images are 100 and 25 µm for ‘Zoom’ panels. (B) Representative bright-field images of DAB-stained coronal brain sections from WT and GS-LRRK2 rats after LPS injection. TH staining and (C) CD68 staining is shown with Nissl staining for contrast. (D) Unbiased stereological quantification of TH+ neurons and (E) CD68+ cells in the SNpc in WT and G2019S LRRK2 LPS-injected rats. (F) Unbiased stereological quantification of Nissl+ neurons. (G) Volume calculation of the tissue area encompassing CD68 cell immunoreactivity. Significance was calculated with one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc comparisons or two-tailed unpaired t-test (F), bars represent group means and error bars are S.E.M. * < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.