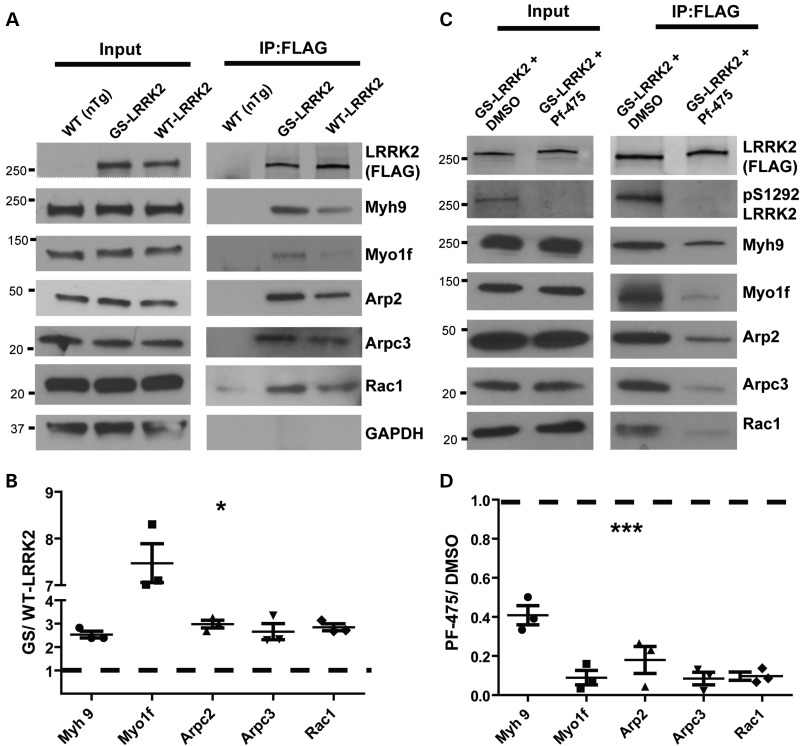
Figure 6.
G2019S LRRK2 enhances interactions with actin regulatory and effector proteins in a kinase-dependent manner. (A) Representative western blots of selected components from LRRK2-positive protein complexes immunoprecipitated from M1 polarized TEPMs. Blots are representative of three independent experiments. (B) Quantification of western blots from (A). Immunoprecipitates from the G2019S LRRK2 pull-down are compared with WT LRRK2 pull-downs that are represented by a dashed line. Fold changes in intensity are indicated (G2019S LRRK2 relative to WT LRRK2). (C) TEPMs were treated with 500 nm PF-06447475 (PF-475) or equivalent vehicle DMSO (0.00005%) for 24 h. Western blots are representative of three independent experiments. (D) Quantification of western blots from (C). Immunoprecipitates from the G2019S LRRK2 + PF-06447475 pull-downs are compared with the G2019S LRRK2 + DMSO pull-downs, represented by a dashed line. Fold changes in intensity are indicated (G2019S LRRK2 + PF-06447475 relative to G2019S LRRK2 + DMSO). Significance was determined by two-tailed one-sample t-tests comparing each fold change against an expected value for no change in the interaction. Bars represent group means, and error bars are S.E.M. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001.