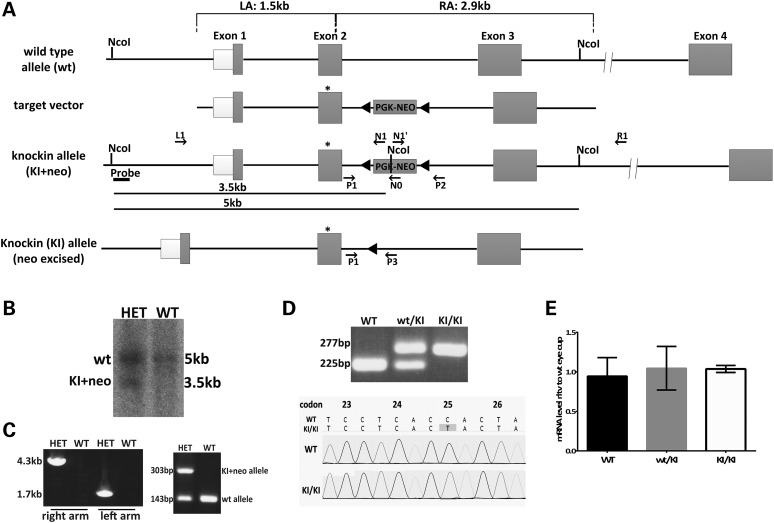
Figure 1.
Generation of a mouse model with Rpe65/P25L mutation. (A) Strategy for targeted insertion of the P25L point mutation into the murine Rpe65 locus to generate a KI mouse model. The targeting vector carried a C to T mutation at codon 25 in exon 2 of Rpe65 (star) and a loxP-flanked neo cassette and included the 1.5-kb flanking sequence from Rpe65 genomic DNA as the 5′ left homology arm (LA) and 2.9 kb as the 3′ right homology arm (RA). The neo cassette was removed by Cre-loxP recombination to generate Rpe65/P25L KI mice. This mouse retained an extra 52-bp sequence with added restriction sites at the loxP site for the convenience of genotyping in intron 2. (B) Southern blot analysis of ES clones after homologous recombination: ES clone genomic DNA was digested with NcoI, followed by hybridization with a 5′ probe outside the LA (Fig. 1A); genomic DNA from the wt allele only shows a 5-kb hybridization signal in WT, whereas homologous recombination gives rise to an additional 3.5-kb fragment owing to the presence of an NcoI restriction site within the neo cassette (Fig. 1A) that is seen in heterozygous animals carrying one copy of the KI+neo allele (HET). (C) Germ-line transmission of the KI+neo allele. Following blastocyst injection, germ-line transmission was identified by long-range PCR of both the LA and the RA (left panel, Fig. 1A and Table 1), and then by simple amplification of a 303-bp amplimer in the HET offspring (right panel) along with a WT 143-bp amplimer, the only one seen in WT (see Supplementary Material, Table S1 for primer sequences). (D) Removal of the neo cassette. The neo cassette was removed via Cre recombinase by crossing F1 heterozygous mice with Zp3-Cre mice carrying a germ-line Cre transgene (24) in the C57B6/J background. PCR primers P1 and P3 were designed to amplify the intron 2 region flanking the 52-bp loxP sequence. The wt allele and KI allele produced 225- and 277-bp PCR products, respectively (top panel; see Supplementary Material, Table S1 for primer sequences). Genomic sequencing confirmed the presence of the C to T mutation at codon P25 in the KI/KI mice (bottom panels). (E) Relative levels of Rpe65 mRNA expressed in eyecups of WT, KI/KI (homozygous) and wt/KI (heterozygous) mice at 16–20 weeks of age as determined by Q-PCR. Expression levels were normalized to two reference genes (Gapdh and Hprt). Error bars indicate SDs from biological triplicates within the experiment.