Table 5.
Relative Rates of Aziridination and C–H Insertion
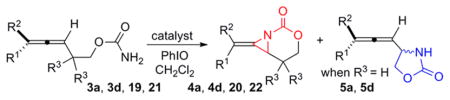
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry | R1-R3 | catalyst (AgOTf, phen) | product(s) | init rate (mmol/min*mL)a |
| 1 | Me, Me, Me 19 |
20 mol%, 25 mol% | 20 | 1.8×10−3 (98% yield) |
| 2 | 10 mol%, 30 mol% | 20 | no reaction | |
| 3 | 20 mol%, 25 mol%, 20 mol% BHT | 20 | 1.4×10−3 (48% yield) | |
|
| ||||
| 4 | Me, Me, H 3a |
20 mol%, 25 mol% | 4a | 1.3×10−3 |
| 5 | 20 mol%, 25 mol%, 20 mol% BHT | 5a | 9.6×10−4 | |
| 6 | 20 mol%, 60 mol% | 5a | 2.8×10−4 | |
| 7 | 20 mol%, 60 mol%, 20 mol% BHT | 5a | 2.1×10−4 | |
|
| ||||
| 8 | C5H11, H, Me 21 |
20 mol%, 25 mol% | 22 | 9.85×10−4 (88% yield) |
| 9 | 20 mol%, 60 mol% | 22 | 36% yieldb | |
| 10 | 20 mol%, 25 mol%, 20 mol% BHT | 22 | 6.15×10−4 | |
|
| ||||
| 11 | C5H11, H, H 3d |
20 mol%, 25 mol% | 4d | 5.73×10−4 |
| 12 | 20 mol%, 25 mol%, 20 mol% BHTc |
4d (26%) 5d (34%) |
3.31×10−4 2.31×10−4 |
|
| 13 | 20 mol%, 60 mol% | 5d | 1.58×10−4 | |
| 14 | 20 mol%, 60 mol%, 20 mol% BHT | 5d | 2.94×10−4 | |
The rate of product formation was monitored by 1H NMR using mesitylene as the internal standards. The indicated initial rates are the average of the three runs, and the standard deviations are included in the SI.
Yield after 21 h, 73% conversion.
The ratio of 4d:5d was 1:1.
