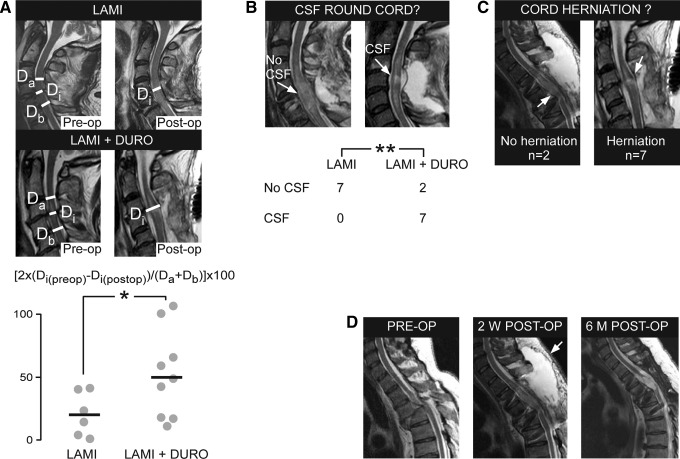
FIG. 2.
Duroplasty increases space round the injured spinal cord. (A) T2 magnetic resonance imaging (MRI; top) before and after laminectomy, and (middle) before and after laminectomy+duroplasty, showing mid-sagittal anteroposterior diameter of the most compressed part of the dura (Di), the anteroposterior diameter of the mid-vertebral dura above the level of injury (Da), and the anteroposterior diameter of the mid-vertebral dura below the level of injury (Db). (Bottom) Percent increase in Di after laminectomy versus laminectomy+duroplasty. Points are patients, lines are means. (B) Top: Post-operative T2 magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) looking for cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) round the injured cord. Bottom: Numbers of patients with and without CSF around the injured cord. (C) Post-operative T2 MRI looking for expansion of the injured cord into the duroplasty. (D) T2 MRI in an American Spinal Injury Association A patient (left) before surgery, (middle) at two weeks after surgery (arrow shows pseudomeningocele), and (right) at six months after surgery (no pseudomeningocele). LAMI, laminectomy; LAMI+DURO, laminectomy+duroplasty. p<0.05*, 0.01**.