FIG. 3.
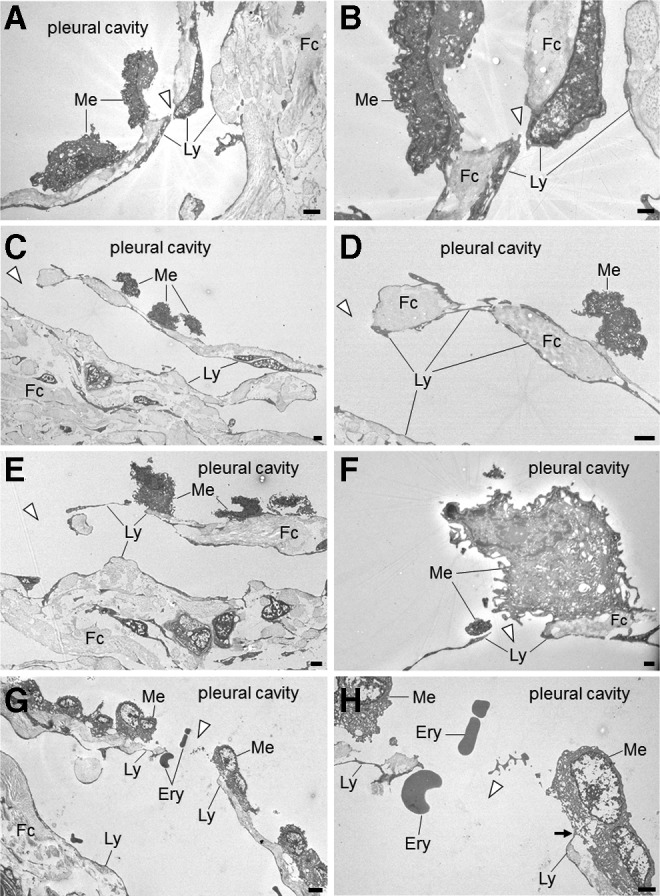
Transmission electron micrographs of the pulmonary ligament. Panels on the right side are enlargements of details presented in the panels on the left. (A) Cuboidal mesothelial cells can be observed on the surface of the serosal membrane. The submesothelial layer consists of fibrous connective tissue, which is discontinuous and interrupted by a stoma (arrowhead). The scale bar indicates 2 μm. (B) A stoma (arrowhead) surrounded by cytoplasm of lymphatic endothelial cells. The scale bar indicates 0.5 μm. (C) A stoma directly continuing into a lymphatic capillary (arrowhead). The scale bar indicates 2 μm. (D) A stoma (arrowhead) and lymphatic endothelial cells surrounding fibrous connective tissue and directly exposed to the pleural cavity. The scale bar indicates 2 μm. (E) A stoma (arrowhead) directly continuing into a lymphatic capillary. The scale bar indicates 2 μm. (F) A stoma composed of thin cytoplasm of a lymphatic endothelial cell adjacent to a mesothelial cell. The scale bar indicates 0.5 μm. (G) A stoma (arrowhead) directly continuing into a lymphatic capillary and erythrocytes passing through a stoma. The scale bar indicates 5 μm. (H) A stoma fringed with lymphatic endothelial cells (arrowhead). On the right side of the stoma, a lymphatic endothelial cell is in contact with a mesothelial cell (arrow). The scale bar indicates 2 μm. Ery, erythrocyte; Fc, fibrous connective tissue; Ly, lymphatic endothelial cell; Me, mesothelial cell.
