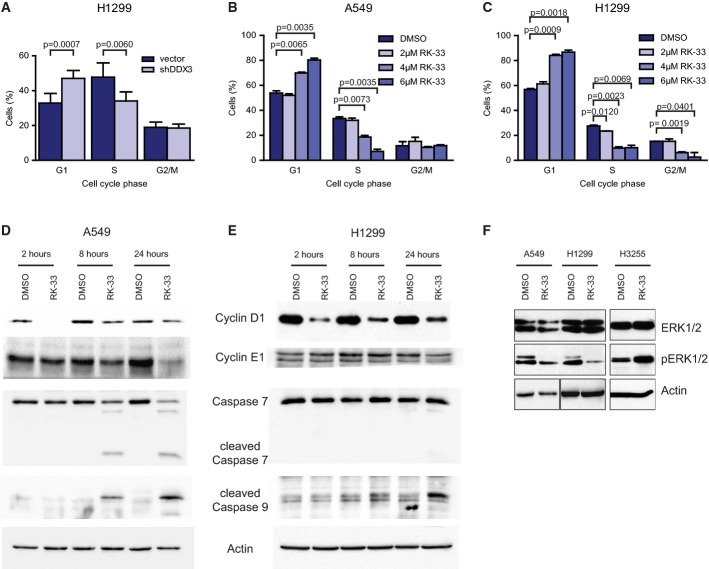
Figure 7.
- A Cell cycle analysis of H1299 cells treated with shDDX3 and processed by flow cytometry. Knockdown of DDX3 led to a decrease of cells in S-phase and an increase of cells in G1-phase, indicative of a G1 arrest. Significance was assessed by two-sided, unpaired t-test. Error bars represent SD.
- B, C Cell cycle analysis of A549 and H1299 cells by flow cytometry after treatment with RK-33 (0, 2, 4, and 6 μM). RK-33 induced a G1 cell cycle arrest in both cell lines. Significance was assessed by two-sided, unpaired t-test. Error bars represent SD.
- D, E Immunoblot of cell cycle-related proteins (Cyclin D1 and Cyclin E1) and cell death-related proteins (cleaved caspase 7, cleaved caspase 9) in A549 and H1299 cells after treatment with RK-33 (10 μM). Initially, a strong decrease of Cyclin D1 was observed. After 8 and 24 h, cleaved caspases 9 and 7 were apparent.
- F Immunoblot of MAPK pathway-related proteins ERK1/2 and phosphorylated ERK1/2 in A549, H1299, and H3255 (RK-33 resistant) cells 24 h after treatment with RK-33 (7.5 μM or 10 μM). ERK2 and especially ERK1 become dephosphorylated after treatment with RK-33 in A549 and H1299 cells but not in H3255 cells. Outlined boxes indicate spliced lanes.
Source data are available online for this figure.