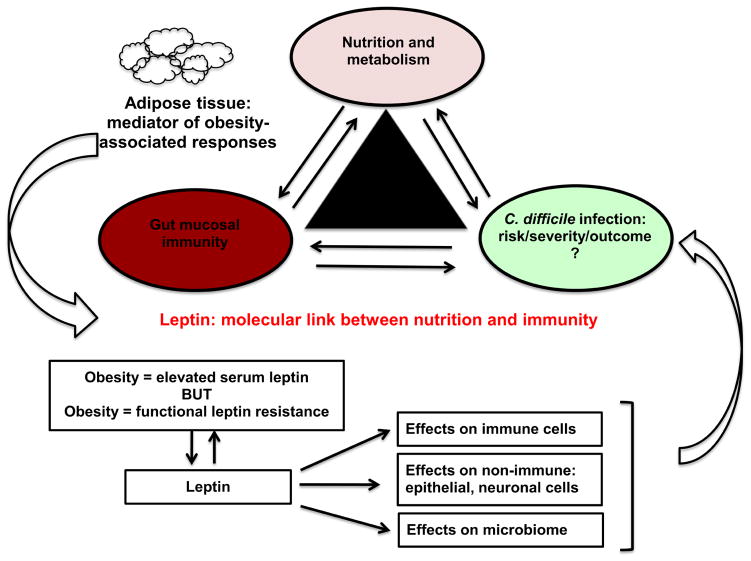
Figure 1. Model of leptin-mediated inflammatory response during C. difficile infections.
Adipose tissue acts as a sensor of host nutritional status and secretes leptin (proportional to body fat). Leptin acts as a molecular link between nutrition and immunity and affects the risk, severity and outcomes of C. difficile infections. The mechanism of leptin actions could be via immune cells, non-immune cells or changes in the host microbiome and since obesity is associated with both elevated leptin levels but also “leptin resistance”, the effects of leptin-mediated actions could lead to diverse effects on the outcomes of C. difficile infections and needs further investigation.