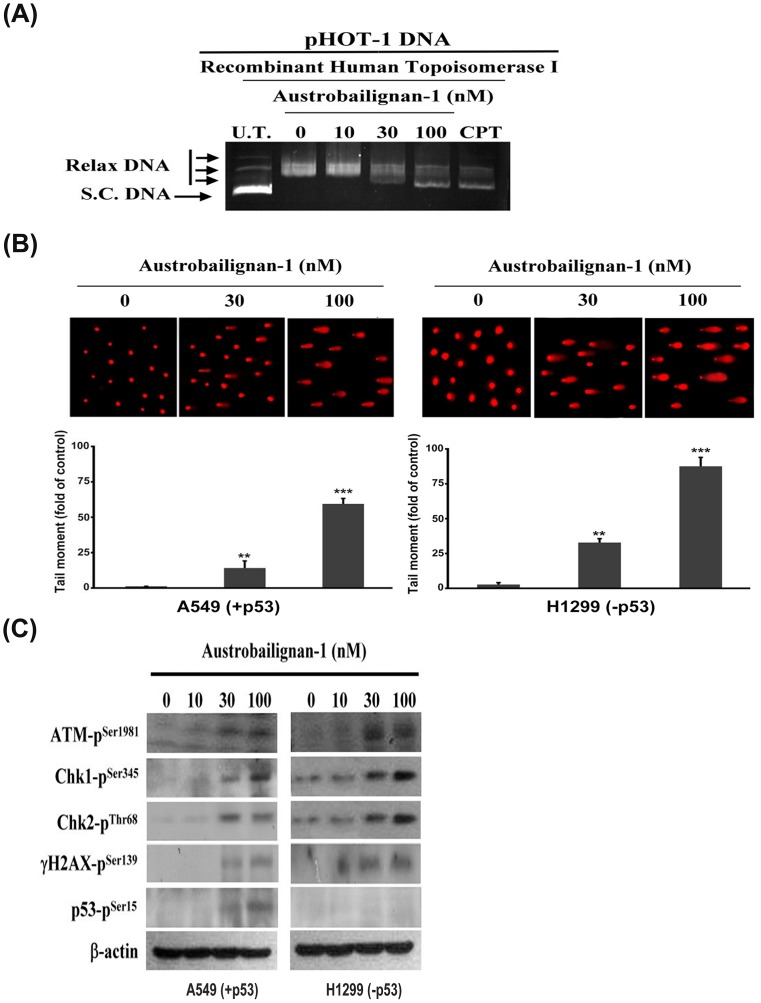
Fig 3. Austrobailignan-1 inhibited topoisomerase 1 activity and induced a DNA damage signaling pathway.
(A) Inhibition of DNA topoisomerase 1 activity. pHOT-1 DNA plasmid was incubated with various concentrations of austrobailignan-1 (0, 10, 30, and 100 nM) and topoisomerase 1 at 37°C for 30 min. The reaction products were separated by 1% agarose gel and stained by ethidium bromide. The fluorescence image was recorded by microphotography. Camptothecin (CPT) was used as a positive control. S. C. DNA: super coiled DNA, Relax DNA: unwind closed circular DNA. (B) DNA damage response. A549 and H1299 cells were treated without or with 30, 100 nM austrobailignan-1 for 24 h, and DNA damage on per cell basis was examined by a comet assay. Representative comet images from the cells exposed to austrobailignan-1 at various concentrations are shown (upper panel). The degree of DNA damage was scored by tail moment (% DNA in tail x tail length) from at least 100 cells in each treatment group (lower panel). Data are mean ± SD for three independent experiments. ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. (C) Activation of ATM signaling pathway by austrobailignan-1. A549 and H1299 cells were treated with various concentrations of austrobailignan-1 for 24 h, the expressed levels of phosphorylated ATM, Chk1, Chk2, H2AX, and p53 proteins were investigated by Western blot analysis. β-actin was used as an internal loading control.