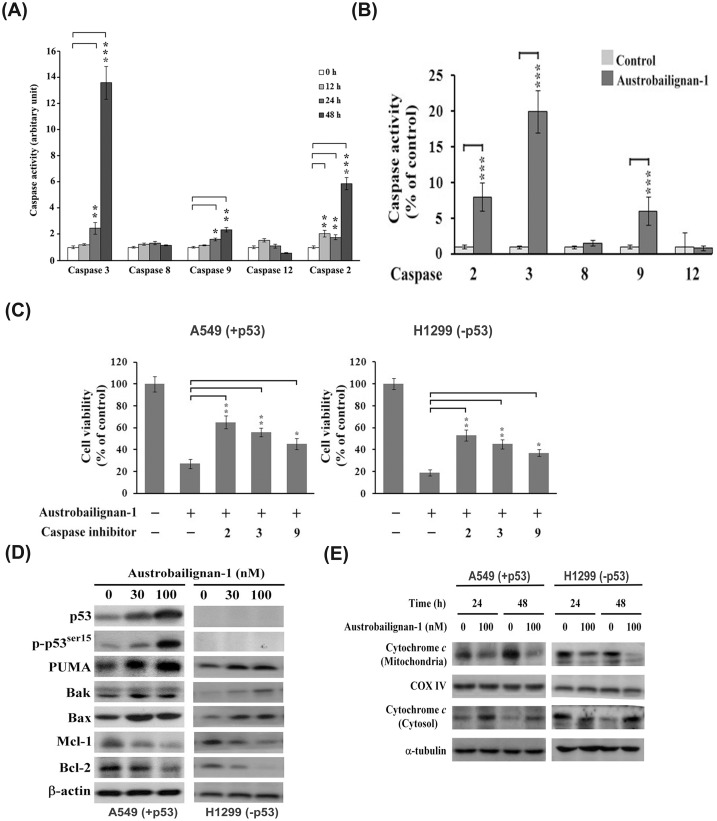
Fig 5. Induction of mitochondrial apoptotic pathway by austrobailignan-1.
(A) A549 cells were treated with 100 nM of austrobailignan-1 for indicated time periods (0, 12, 24, and 48 h). (B) H1299 cells were exposed to austrobailignan-1 for 48 h. The cell lysates were harvested, and the caspase activities were determined using fluorogen substrates. Data are expressed as mean ± S.D. from three independent experiments. (*P <0.05,** P <0.01, *** P < 0.001 v.s. vehicle-treated control). (C) Caspase inhibitors block austrobailignan-1-induced cell death. A549 and H1299 cells were pretreated with 50 μM indicated caspase inhibitors for 1 h, and then treated with 100 nM austrobailignan-1 for another 48 h. The cell viability was measured by a Trypan blue dye exclusion method. (D) Regulation of Bcl-2 family proteins. A549 and H1299 cells were treated with 0, 30, 100 nM austrobailignan-1 for 48 h. The levels of indicated Bcl-2 family proteins were examined by Western blot. (E) Release of cytochrome c from mitochondria to cytosol. A549 and H1299 cells were treated without or with 100 nM austrobailignan-1 for 24 and 48 h. After treatment, particulate and cytosolic fractions were isolated, the level of cytochrome c protein was analyzed by Western blot. α-tubulin and cytochrome oxidase IV were used as loading control.