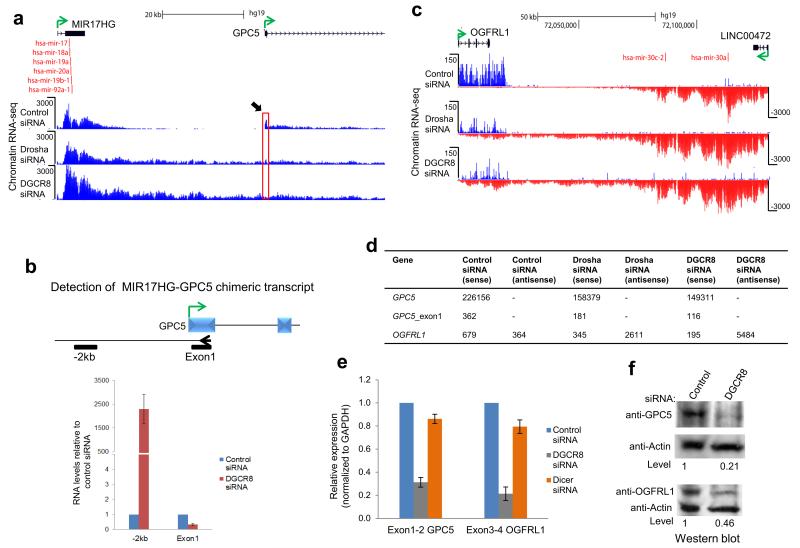
Figure 7. Microprocessor dependent termination prevents transcriptional interference.
a. Chromatin RNA-seq profiles across MIR17HG-GPC5 tandem gene locus showing readthrough transcription following Microprocessor depletion. Black arrow and red box highlights reduction in GPC5 exon 1 peak following Microprocessor depletion. b. RT-qPCR analysis of chimeric transcripts versus GPC5 exon 1. Gene specific RT primer (arrowhead) in exon 1 and PCR amplicons are indicated by black bars. c. Chromatin RNA-seq profiles across convergent OGFRL1-LINC00472 gene locus. d. Read quantification for protein coding genes subject to transcriptional interference following Microprocessor depletion. e. mRNA levels of GPC5 and OGFRL1 were determined by RT-qPCR using exon specific primers. RNA levels are expressed relative to control siRNA which were set to 1. All values are normalized to GAPDH mRNA. f. Protein levels of GPC5 and OGFRL1 are reduced by transcriptional interference. Direction of transcription is indicated by green arrow and miRNA by red vertical lines. All experiments used HeLa cells. Error bars represent s.d. of an average (n=3 independent experiments).